Section 4: Sample Selected-Response Questions Special Education Specialist EC–12 (186)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for you to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied by the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements do not appear on the actual exam.
The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will see on the exam; however, your performance on the sample questions should not be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual exam.
Selected-Response Questions with Rationales
Each sample exam question here includes the correct answer and a rationale for each answer option.
Domain I—Legal and Ethical Guidelines and Knowledge of Learners
Competency 001—(Legal and Ethical Guidelines): Apply knowledge of applicable state and federal laws and procedures that pertain to special education services.
1. After an Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting for a student with an intellectual disability (ID), the student's parent/guardian mentions that they would like a caseworker who provides services to their child to receive a copy of their child's Individualized Education Program (IEP) from the school. Which of the following actions should the special education teacher take to share the student's IEP safely and securely with the caseworker?
- asking the parent/guardian to provide reasons for why the caseworker needs a copy of the student's IEP
- telling the parent/guardian that the school can provide a copy of the student's IEP to the caseworker only with written permission from the student's parent/guardian
- letting the parent/guardian know that the school can provide the caseworker with a written summary of the ARD committee meeting instead of the student's IEP
- contacting the caseworker and inviting them to the school campus to review the student's IEP
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because a student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) is part of the student's education record. The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law that protects the privacy of students' education records. The law applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicable program of the U.S. Department of Education. FERPA gives parents/guardians certain rights with respect to their children's education records, including the right to request that their child's education record is released to others, if the parent/guardian provides written permission for the release. There are some situations in which FERPA allows schools to disclose education records without written consent (e.g., to school officials with legitimate educational interest, to comply with a judicial order or lawfully issued subpoena). Option A is incorrect because the special education teacher does not need to know why the parent/guardian is requesting the IEP for the caseworker, and the reason for sharing it alone would not provide legal permission to disclose the IEP to the caseworker. Option C is incorrect because telling the parent/guardian that the school can provide the caseworker with a written summary of the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting would satisfy the parent's/guardian's request but would not provide the caseworker with all of the information included in the student's IEP. A written summary of the ARD committee meeting may also include information protected under FERPA and would be in violation of federal law. Option D is incorrect because it would be illegal to invite the caseworker to review the student's IEP without first obtaining written permission from the student's parent/guardian.
Competency 002—(Knowledge of Learners): Apply knowledge of understanding how to address each student's developmental, communication, and learning needs.
2. A special education teacher co-teaches in a fourth-grade classroom. The special education teacher and general education teacher notice that a student who had been working at grade level for the first half of the school year has started turning in homework and classwork assignments late. The student frequently puts their head down on the desk and has fallen asleep during class on more than one occasion. When the teachers ask the student about the recent changes in their behavior and classwork, the student reports that they cannot complete their classwork due to fatigue resulting from frequent arguments in their home environment. The student mentions that their parents/guardians argue loudly for many hours each night and the student has difficulty sleeping. Which of the following approaches would be most effective for the teachers to take with the student?
- working with the school counselor to develop supports for the student within the classroom and school environment
- inviting the student's parents/guardians to school to discuss creating a plan that would help their family
- providing the student with additional academic stimulation and more challenging assignments
- requesting that the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee conduct a functional behavioral assessment (FBA) with the student
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because certified school counselors can provide a comprehensive school counseling program in accordance with Chapter 33 of the Texas Education Code to all students, including students receiving special education services, and can also serve on the Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) team. Collaborating with the school counselor in this way can allow the special education teacher to provide more comprehensive supports to the student. Option B is incorrect because it is not the special education teacher's role to develop plans with families related to families' personal matters. Option C is incorrect because there is no evidence that the student needs more stimulation or more challenging assignments. Providing these supports to the student would not be useful in reducing the student's fatigue or stress. Option D is incorrect because none of the conditions necessary under federal or state law to request a functional behavioral assessment (FBA) have been met in this situation.
Domain II—Assessment and Program Planning
Competency 003—(Assessment for Data-Driven Decision Making): Apply knowledge of the evaluation and assessment process and of appropriate assessment strategies to inform instructional design and to support students.
3. To promote students' reading fluency, a special education teacher plans activities in which fifth-grade students with specific learning disabilities in reading fluency partner to engage in repeated oral readings. When the teacher assembles the reading materials for the activities, the teacher should assign each pair of students passages from a text that:
- both students are capable of reading aloud with few word-recognition errors.
- the students have previewed and selected themselves.
- both students have been reading in connection with content-area study.
- contain vocabulary and concepts that the students will need to have mastered by the end of the year.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because fluency develops as a result of students having many opportunities to practice reading texts with words that they can decode easily or that they already know and that is at their independent reading level. The best strategy for developing reading fluency is to provide students with many opportunities to read the same passage orally several times. Fluency is the ability to read a text quickly, accurately, and with expression. Fluency builds stamina for reading long or complex text. Fluency connects word recognition and comprehension because fluent readers do not have to focus on decoding words but instead can focus on understanding text meaning. Option B is incorrect because even though it is important to involve students in selecting texts so they are interested in reading them, this practice does not ensure that the level of the text will be appropriate to support building the students' fluency. Option C is incorrect because the texts that are chosen do not need to be related to content-area study but instead must be at the students' independent reading level. Option D is incorrect because the texts used should contain vocabulary and concepts that the students already understand, not that they will learn by the end of the school year.
4. A sixth-grade student with an intellectual disability (ID) struggles to independently complete multistep mathematics problems. A task analysis shows that the student frequently has difficulty utilizing steps that help with recalling multiplication facts. The student can complete the problem by referencing a multiplication table or receiving a teacher prompt. Which of the following statements is the best way to describe the student's present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) in this area on the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP)?
- The student has difficulty completing multistep mathematics problems and completes 20 percent of problems independently without accommodations. With the aid of a multiplication table or teacher prompt, the student can complete at least 90 percent of multistep mathematics problems accurately.
- The student benefits from referencing a multiplication table and receiving a teacher prompt when completing multistep multiplication problems.
- When working independently without accommodation, the student completes 20 percent of multistep mathematics problems accurately.
- The student has difficulty remembering the steps involved in solving multistep mathematics problems. With assistance, the student completes 90 percent of multistep mathematics problems accurately.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the student's present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) is a statement in a student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) that provides information on how the student's disability affects their involvement and progress in the general education curriculum. A PLAAFP is the foundation on which to build the student's IEP and should include components such as clear and objective baseline data and a description of the student's strengths, needs, and skill gaps. Other important components of a PLAAFP are an explanation of how gaps affect the student's learning and participation, an explanation of how the student's disability impacts their progress in the general curriculum, and information that the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee uses to determine what the student can achieve in one year. Option B is incorrect because it does not provide baseline data on the student or information on the student's needs or skill gaps. Options C and D are incorrect because they do not provide information about the multiplication tables or teacher prompts that support the student's progress in this area, which are important to know when considering what supports the student uses.
Competency 004—(Developing, Implementing, and Monitoring Individualized Programs): Apply knowledge of contributing to, monitoring, and reporting on individualized programming for students.
5. A first-grade teacher and a special education teacher administer a midyear universal screener to each student in their class. Screener results for a student diagnosed with dyslexia are shown below.
Subtest Percentile Letter-Sound Fluency 15 Nonsense Word Reading 7 Word Identification 21 Oral Reading Fluency 24
A targeted intervention in which of the following areas would likely yield the most significant results in the student's decoding abilities?
- letter-sound automaticity
- word family sorts
- phrasing and prosody
- irregular word reading drills
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the student received the lowest score in Nonsense Word Reading and would benefit most from work in this area. Nonsense words are letter sequences that follow regular phonetic words and are pronounceable but have no meaning, such as yom, mig, or bif. By working on letter-sound automaticity, the student would improve in decoding regular phonetic words. Option B is incorrect because word family sorts are activities in which students recognize word patterns and learn about onset and rime. During these activities, students create or choose groups of words that have the same rime but different onset. This activity would not support the student's needs because the student first needs to develop letter-sound automaticity and the student scored higher in word identification skills. Option C is incorrect because the student scored highest in oral reading fluency, which includes reading with phrasing and prosody, which are oral reading fluency components of reading quickly, accurately, and with expression. Option D is incorrect because irregular words such as said, what, and they do not follow typical letter-sound rules, and memorizing them would not support the student's letter-sound automaticity needs.
6. An eleventh-grade student with an intellectual disability (ID) has the following Individualized Education Program (IEP) goal.
By the next annual IEP, when given a list of 10 functional safety sight words, the student will orally read the words with 90% accuracy for 4 out of 5 consecutive data collection days.
Each day, the teacher shows the student the words and corresponding safety symbols on flash cards and asks the student to repeat the words in order to develop recognition mastery. The student's recognition results are shown below.
IEP Goal Progress Monitoring Data
Key: ** = baselineDate 9/10
**9/11 9/12 9/13 9/14 9/17 9/18 9/19 9/20 9/21 Percent Accuracy 50% 40% 50% 55% 40% 45% 55% 50% 45% 50%
After reviewing the results in the progress monitoring chart, which of the following actions should the teacher take?
- scheduling an IEP review meeting with the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee to rewrite the IEP goal
- trying different instructional approaches to see if better results can be achieved with the student
- adding additional safety symbols to the flash card activity and continuing to record progress monitoring data
- repeating the same activity with the student for a few more weeks to see if the student makes measurable improvement
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because based on the data collected, the student is not making progress with the flash card instructional approach that is currently used. Trying another instructional approach with the student and collecting data on the student's progress with the new approach would be a useful step to take next to support the student's progress toward the goal. Option A is incorrect because the special education teacher should try additional approaches with the student before requesting an Individualized Education Program (IEP) review meeting with the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee to determine if another approach would work better or to gather additional data about why the IEP goal should be rewritten. Option C is incorrect because adding additional safety symbols to the activity would make the activity more difficult for the student and would not increase the activity's effectiveness. Option D is incorrect because the student has not made any lasting progress using the flash card intervention, and it is unlikely that this intervention will begin to be effective after two weeks of no progress.
7. A special education teacher who works with tenth- and eleventh-grade students reminds students about the college fair that will be happening on campus later that week. A student receiving special education services for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has moderate difficulty with academic and social skills but has expressed interest in continuing to develop academic skills after high school. The teacher has the following conversation with the student.
Teacher: Are you going to the college fair this evening?
Student: No.
Teacher: Oh, I thought I would see you there. I think you would learn a lot about options for after graduation.
Student: No, I talked to my parents last night and they said college isn't for our family.
The day after the college fair, the teacher confirms that this student did not attend the college fair. Which of the following actions should the teacher take to best support the students and facilitate a wide range of options beyond high school for them?
- recommending students take a self-assessment inventory of strengths and challenges to inform their postsecondary options
- providing materials to educate students and their parents/guardians about on-the-job training, programs, and funding options at colleges that would be a good fit for the student
- encouraging parents/guardians to allow their children to attend future college fairs because it is a useful opportunity to practice social skills in an unstructured setting
- contacting local businesses that provide volunteer opportunities for young adults and asking the businesses to identify job openings
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because it is important for special education teachers to ensure students and their families are aware of all the options that are available after graduation. The student has expressed interest to their teacher in continuing to develop academic skills after high school, and therefore the teacher should provide the student and their parents/guardians with information about how the student can access college and/or other programs that would support their post-graduation goals. Option A is incorrect because asking the student to take a self-assessment inventory of their strengths and challenges would potentially provide more information about the student but would not support the student and their family in understanding the wide range of options that are available after graduation. Option C is incorrect because encouraging the parents/guardians to allow their child to attend future college fairs does not mean that there will be more college fairs for the student to attend or that the student will be able to attend. Option D is incorrect because asking local businesses to identify job openings for young adults does not ensure that the student will have an interest in working with those businesses and does not provide information on a range of opportunities for the student, only those with the businesses contacted.
8. A special education teacher is working with a tenth-grade student who receives special education services for an orthopedic impairment (OI). The student has limited mobility and difficulty with some fine-motor skills. The student uses a wheelchair on campus, often with assistance, and plans to attend college upon graduation.
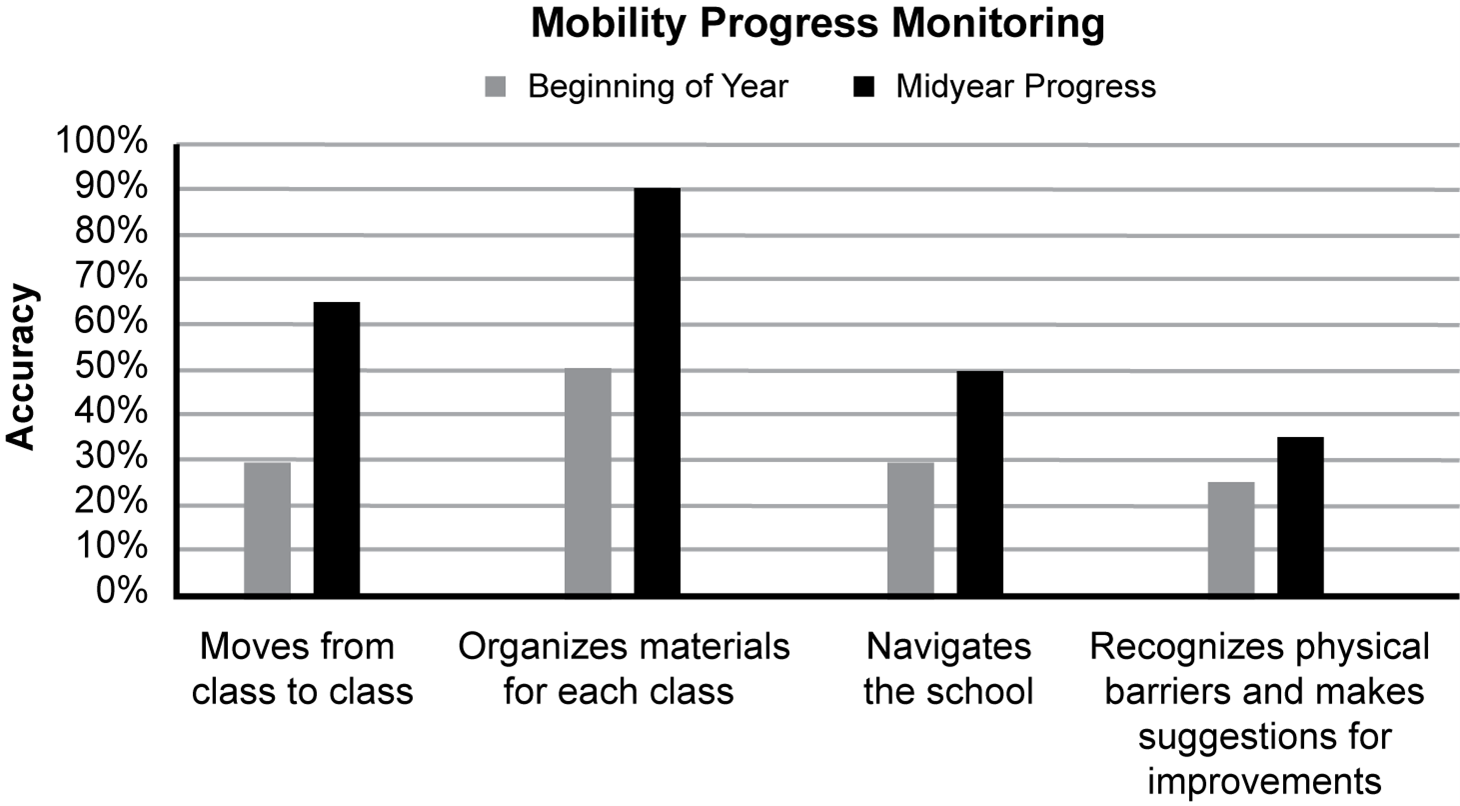
The bar graph measures two variables, beginning of year and midyear progress. The skills that are measured are moves from class to class, organizes materials for each class, navigates the school, and recognizes physical barriers and makes suggestions for improvements. In moving from class to class, the student achieved 30% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 65% accuracy midyear. In organizing materials for each class, the student achieved 50% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 90% accuracy midyear. In navigating the school, the student achieved 30% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 50% accuracy midyear. In recognizing physical barriers and making suggestions for improvements, the student achieved 25% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 35% accuracy midyear.
Based on the information provided, which of the following Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals will best prepare the student for postsecondary readiness?
- By the next IEP, the student will demonstrate the ability to self-advocate by identifying mobility barriers and possible suggestions for improvement with 80% accuracy in nine out of ten opportunities.
- By the next IEP, the student will demonstrate the ability to travel independently in and around the campus setting without assistance with 100% accuracy in nine out of ten attempts.
- By the next IEP, the student will demonstrate the ability to move from one classroom to another within the allotted transition period with 80% accuracy in nine out of ten attempts.
- By the next IEP, the student will demonstrate the ability to demonstrate organizational and self-care skills necessary for success in an advanced educational setting with 100% accuracy in nine out of ten opportunities.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the student plans to attend college upon graduation and will need to be able to navigate independently. The student has demonstrated progress in moving from class to class and in navigating the school, and traveling in and around campus is the next skill for the student in independent travel. Option A is incorrect because although it is important for the student to recognize physical barriers and make suggestions for improvements, this skill would not directly promote the student's independence or travel skills for postsecondary readiness. Option C is incorrect because the student is already demonstrating the ability to move from class to class with 65% accuracy, and so this would be a repetition of a goal the student is already working on. Option D is incorrect because the student is already demonstrating the ability to organize materials for each class with 90% accuracy. Additionally, the question does not mention that the student needs to learn self-care skills.
Domain III—Curricular Knowledge and Instructional Practices
Competency 005—(Subject Matter Content and Specialized Instructional Strategies): Apply knowledge of implementing curriculum through relevant and appropriate content and specialized instructional strategies to guide and support students' learning and development.
9. A special education teacher co-teaches in a prekindergarten classroom. The teacher is working with a child on the following outcome from the Texas Prekindergarten Guidelines.
PK4 Outcome PK4.IV.A.1. Child intentionally uses marks, letters, or symbols to record language and verbally shares meaning. Child Behaviors The child may:
- use letter-like shapes when writing or making labels in learning centers
- attempt to write letters to represent a word as a caption under a drawing and "reads" it to an adult or peer
- write a story or message using mock letters, symbols, or other marks and "reads" it to the teacher
- label pictures to tell a story
The child with whom the teacher is working is four years old and has been identified as having a Non-Categorical Early Childhood (NCEC) eligibility. Currently, the child makes marks and scribbles on paper but has not demonstrated an awareness that the marks are related to language. Which of the following activities by the special education teacher would best support the child in meeting the objective of this End of Prekindergarten Year Outcome?
- asking the child to sound out words in a beginning-level reader
- providing a sensory table in which the child can explore different textures of materials
- modeling think-aloud behaviors that describe to the child what the teacher is thinking about while writing words
- reading to the child and asking the child to point to associated pictures
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the PK4 Outcome the teacher is working on with the child involves the child intentionally using marks, letters, or symbols to record language and verbally sharing meaning. When the teacher models think-aloud behaviors that describe to the child what the teacher is thinking about when writing words, the teacher is showing the child how letters, which are marks on a page, can have meaning and convey what a person is thinking. This action makes a concrete connection for the child for an abstract concept–recording thoughts through making marks, letters, or symbols on a page. Option A is incorrect because sounding out words is a reading skill, and the question relates to prewriting and writing skills. Option B is incorrect because although exploring textures of materials can promote tactual skills, this activity does not support skills related to understanding that marks on a page convey meaning. Option D is incorrect because asking the student to point to pictures in a story while they listen as it is read aloud to them promotes the child's connection to and comprehension of the story. However, this approach does not support the child's development of making marks, letters, or symbols to record language and verbally sharing meaning of what they have written.
10. A special education teacher is collaborating with a general education teacher to adapt science instruction for a fourth-grade student with a mild intellectual disability (ID) during whole-group and small-group lessons. The student understands that objects have properties and patterns. The student is working toward understanding the concept of matter and that matter has measurable physical properties and different states. The student understands that force causes an object to move. The student is working toward understanding that force, motion, and energy are related and that energy exists in many forms. Which of the following approaches is the best practice for adapting instruction for the student in an inclusion setting?
- providing the student with instruction using Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) corresponding to their skill level rather than grade level after whole-group instruction
- recommending that the student participate in the whole-group direct instruction in the associated Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) from the special education teacher
- assessing the student on specific, targeted Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) if the whole-group and small-group lessons do not meet the student's learning needs
- supplementing whole-group instruction with small-group or individual instruction based on Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Vertical Alignment access points
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Vertical Alignment access points support understanding the progression across the continuum of learning in various content areas. The special education teacher and general education teacher can apply what the student knows and understands in science to the Science Vertical Alignment to determine what to teach the student next and how to provide instruction that will support the student's next level of learning. Option A is incorrect because providing the student with instruction using Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) corresponding to their skill level rather than grade level after whole-group instruction does not allow the teachers to individualize or adapt instruction. Option B is incorrect because asking the special education teacher to provide direct instruction in grade-level TEKS is not an approach for adapting instruction for the student, and this approach will not be accessible to the student in the same way that approaches from the Vertical Alignment will be. Option C is incorrect because assessing the student on specific, targeted TEKS skills is not a method to use to provide adapted instruction.
11. A special education teacher works as a member of an Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee for a ninth-grade student with a specific learning disability (SLD) in mathematics calculation and mathematics problem solving. The ARD committee is drafting mathematics Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals for the student. The student has been receiving instruction on a fifth-grade level in the special education classroom. The teacher monitors the student's progress through their demonstrated proficiency on work samples and assessments. The special education teacher reviews the Vertical Alignment of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for comparing and ordering numbers and summarizes related progress monitoring data about the student's current competencies.
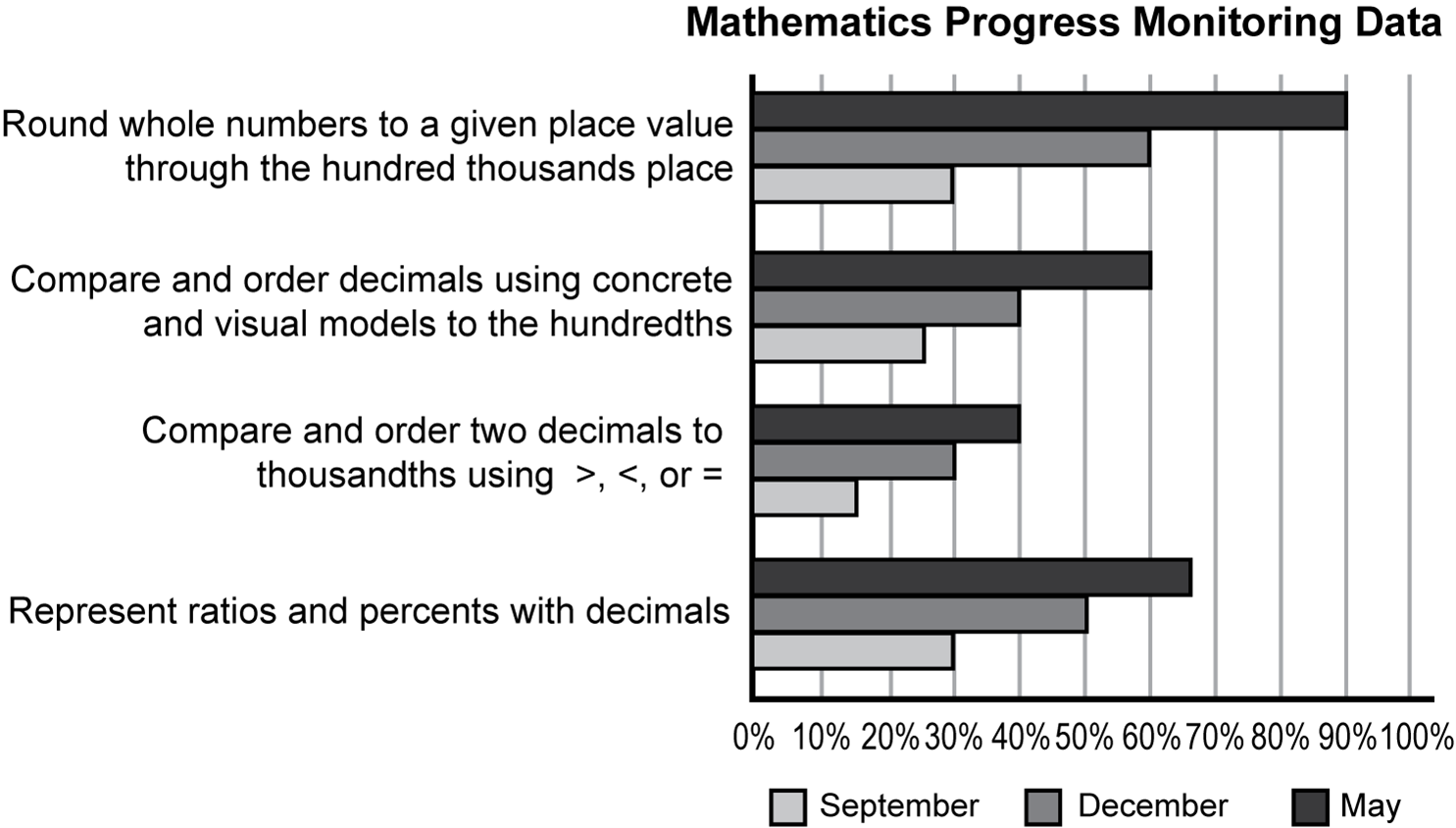
The bar graph measures three variables which are progress in September, progress in December, and progress in May. The skills that are measured are round whole numbers to a given place value through the hundred thousandths place; compare and order decimals using concrete and visual models to the hundredths; compare and order two decimals to thousandths using a greater than symbol, a less than symbol, or an equal symbol; and represent ratios and percents with decimals.
The student's progress in rounding whole numbers to a given place value through the hundred thousands place was 30% accuracy in September, 60% accuracy in December, and 90% accuracy in May. The student's progress in comparing and ordering decimals using concrete and visual models to the hundredths was 25% accuracy in September, 40% accuracy in December, and 60% accuracy in May. The student's progress in comparing and ordering two decimals to thousandths using a greater than symbol, a less than symbol, or an equal symbol was 15% accuracy in September, 30% accuracy in December, and 40% accuracy in May. The student's progress in representing ratios and percents with decimals was 30% accuracy in September, 50% accuracy in December, and 65% accuracy in May.
Which of the following IEP goals and explanation for the IEP goal would be most appropriate for the student?
- By the next annual IEP, given sets of five decimals and concrete models, the student will order the numbers from least to greatest with 80% accuracy in four out of five work samples. This goal brings the student closer to grade level, better preparing the student for the Algebra I end-of-course exam.
- By the next annual IEP, given sets of five whole numbers, the student will round the numbers to a given place value through the hundred-thousands place with 80% accuracy in four out of five work samples. This goal would require the student to maintain a previously mastered, essential skill during the next school year.
- By the next annual IEP, given sets of two decimal numbers, the student will compare and order the numbers using greater than, less than, or equal symbols with 80% accuracy in four out of five work samples. This goal promotes progress toward mathematics TEKS and College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) for Mathematics.
- By the next annual IEP, given sets of decimals, the student will represent ratios and percentages using these decimals with 80% accuracy in four out of five work samples. This goal would support the student in complete mastery of the Grade 5–level TEKS and prepares the student for success at the next level.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the student's progress monitoring data show that the student was able to compare and order two decimals to thousandths using greater than, less than, or equal to with 15% accuracy in September, 30% accuracy in December, and 40% accuracy in May. Of the areas in which the special education teacher has been collecting progress monitoring data on the student, this is the area in which the student demonstrates a need for continued instruction and support. This Individualized Education Program (IEP) goal promotes both the student's progress toward Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) in an area in which they would benefit from additional skills. Option A is incorrect because the student's progress monitoring data show they are demonstrating significant growth toward their IEP goal of comparing and ordering decimals to the hundredths place, from 25% accuracy in September to 40% accuracy in December to 60% accuracy in May. Option B is incorrect because the student has exceeded their 80% accuracy goal of rounding numbers to a given place value through the hundred-thousands place by demonstrating 90% accuracy in this area in May. Option D is incorrect because the student is making significant progress with representing ratios and percents with decimals, as demonstrated in their progress monitoring data growth from 30% accuracy in September to 50% accuracy in December to 65% accuracy in May.
12. A special education teacher in a middle school self-contained classroom is preparing curriculum recommendations for a current student in an upcoming Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting. Which of the following actions should the special education teacher take first for this purpose?
- basing recommendations for modifications of curricula on assessment data and work samples received from the student's general education teachers and on current research on students with similar needs
- selecting assessment methods to monitor the student's progress toward academic and functional living skills in the modified curriculum
- talking with the student's parents/guardians to find out which modifications they would like to recommend for consideration by the ARD committee
- using the student's present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) to determine appropriate individualized support and modifications to the general education curriculum
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because in order to provide curriculum recommendations for a student, the special education teacher must be able to report on what the student knows and can do. The student's present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) contains information about what the student presently knows and can do based on data collected through special education evaluation and is the basis and starting point for writing a student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals. The teacher works with the student in a self-contained classroom, and the PLAAFP can provide information about what types of individualized support and modifications to the general education curriculum are necessary for the student. Option A is incorrect because the special education teacher should provide recommendations primarily on what they observe and document in their work with a student. Information provided by others can be helpful but must be validated by the student's special education teacher for them to provide recommendations. A teacher should not make recommendations based on research on similar students but on the student themselves and the student's progress monitoring data. Option B is incorrect because the special education teacher needs to provide information about the student based on what has already been assessed and observed through evaluation data. Selecting assessment methods does not provide data on the student but using assessments with the student and compiling this information in a PLAAFP does. Option C is incorrect because although it is important to consult with parents/guardians on modifications that they think would be beneficial for their child, it is necessary for the special education teacher, who is trained in this area, to use information about the student's PLAAFP to make this determination accurately.
Competency 006—(Supporting Learning Using Effective Instruction): Apply knowledge of diverse strengths and needs of students to plan appropriate, effective, meaningful, and challenging instruction.
13. An eighth-grade student who receives special education services for a specific learning disability (SLD) in mathematics problem solving and reading comprehension has difficulty understanding and solving word problems. The student's preferred learning modality is kinesthetic-tactile learning. Which of the following scaffolds would benefit the student when completing a set of word problems involving volume?
- teaching the student to draw out the shapes in the word problems
- hanging measurement formula charts for the student to refer to when thinking about mathematics concepts
- modeling for the student the steps to take to complete the number sentence for the first problem
- providing the student with manipulatives and models to complete the work
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because based on the student's preferred learning modality touching or manipulating materials would best support their learning. Manipulatives are physical objects such as small blocks, shapes, counters, and pieces of paper that are used to represent numbers. Models in mathematics are replicas of shapes or objects that are being studied, and students can use them to represent abstract mathematical operations or to touch and explore a geometric shape. Options A and B are incorrect because drawing shapes creates a visual representation and hanging measurement formula charts provide a visual representation, both of which do not support the student's preferred learning modality. Option C is incorrect because modeling for the student how to complete the problem provides auditory and visual support but does not support the student's preferred learning modality.
Competency 007—(Supporting Social, Behavioral, and Emotional Growth): Apply knowledge of strategies to create effective and safe learning environments, methods to promote students' positive behavior, and supports to develop and measure behavioral interventions.
14. A third-grade student diagnosed with cerebral palsy (CP) has a visual impairment (VI) and limited mobility that requires the use of a wheelchair. The student's special education and general education teachers consult with the occupational therapy specialist, physical therapist, and vision specialist to design a classroom environment that will best support the student's needs. This student would benefit most from which of the following attributes of an environment aligned with universal design for learning (UDL) principles?
- noise-canceling headphones and sensory items to provide options for the student's self-regulation and coping skills
- flexible seating during independent work to optimize the student's individual choice and autonomy
- clearly posted objectives to promote the student's participation in classroom expectations
- ample space in each area of the classroom and multiple ways to retrieve materials to optimize the student's access
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because it is important for the student to have access to the physical space in the classroom. It is also important for the student to have multiple ways to retrieve materials (e.g., auditory access, physical access at an appropriate height for the student) due to potential visual and physical needs. Option A is incorrect because noise-canceling headphones and sensory items would benefit a student with self-regulation and coping skill needs, but this student has not identified as having either of those needs. Option B is incorrect because flexible seating to benefit individual choice and autonomy is beneficial to many students, but the question does not provide any information that these factors would specifically benefit this student. Option C is incorrect because clearly posted objectives do not benefit a student with a visual impairment unless they are visually accessible to the student.
15. A high school is implementing a positive behavioral interventions and supports (PBIS) plan schoolwide to promote students' social competence and contribute to a positive learning environment. As a part of the school's Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS), the school administers a variety of screenings to students to identify possible needs. Which of the following outcomes is the greatest benefit of the screenings?
- providing a means for identification of students who may benefit from supports provided through an MTSS process
- identifying successful Tier 1 practices the school is considering implementing for all students
- providing information about students needing Tier 2 and Tier 3 supports to achieve academic success
- identifying a way for the school to see the range of learning gaps of students in the school
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because screening is often recognized as a foundational component of a comprehensive, multi-tiered system of school-based supports. It is important for schools to monitor students in a variety of domains, including academic skills, physical health, social skills, and behavioral health. Option B is incorrect because screenings would not be used to identify successful practices or approaches. Option C is incorrect because screenings provide preliminary information about students who should be assessed further and do not provide adequate information to identify the level of support that a student needs. Option D is incorrect because screenings should not be used to compare students to each other or to make judgments or decisions about the school's needs as a whole.
Domain IV—Professional Collaboration, Learning, and Responsibilities
Competency 008—(Consultation and Collaboration): Apply knowledge of strategies, approaches, and techniques for effective consultation and collaboration with students, parents/guardians, school personnel, and other professionals to support students' development and learning.
16. A special education teacher is preparing to work with a new paraprofessional at the beginning of the school year. The paraprofessional is new to the job and the teacher wants to ensure the paraprofessional feels supported. Which of the following actions should the teacher take first with the paraprofessional for this purpose?
- providing the paraprofessional with the Individualized Education Program (IEP) of each student whom they will be working
- asking the paraprofessional to come prepared with a self-reflection journal in which they will record their strengths and challenges
- meeting with the paraprofessional to discuss the expectations of their role and daily schedules of the activities they will support
- giving the paraprofessional a copy of their employment contract that outlines their responsibilities
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because paraprofessionals provide instructional support to students, and it is important for them to understand their role with individual students in each classroom and learning environment and to know and understand what they will work on with students each day. Making sure paraprofessionals are informed about their job expectations and that they understand the students they work with supports their success with students. Option A is incorrect because while it is important for the paraprofessional to know the Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals they will be working on with students and also to know the students' accommodations, modifications, and information about other supports they will provide each student, providing the paraprofessional with the daily expectations and schedules should be the first action taken by the teacher. In addition, paraprofessionals should not have access to the IEP itself and only need access to information that allows them to effectively support the student. Option B is incorrect because although self-reflection can support professional development and knowledge of oneself, it does not provide direct support to the paraprofessional from others. Option D is incorrect because the paraprofessional should already have received a copy of their employment contract and although this provides them with information about their job responsibilities, it does not outline specific information about daily expectations or schedules.
17. A special education teacher co-teaches in a fifth-grade classroom and works with a student who is deaf and wears cochlear implants. The special education teacher has been providing interventions and accommodations to the student from their Individualized Education Program (IEP) for several months during reading lessons. The student is not making adequate progress on their reading IEP goals based on their most recent progress report. Which of the following approaches would be most effective for the special education teacher to take first in this situation?
- providing the student with additional assistive technology, such as an FM system and real-time transcription, and asking that these types of assistive technology are added to the student's IEP
- meeting with the teacher of the deaf and hard of hearing (DHH) to ensure that accommodations are provided appropriately and convening the student's Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee to review and revise the student's IEP goals if needed
- suggesting that the student's parents/guardians come to the school to observe the student's reading lessons and provide feedback to the special education teacher and teacher of the deaf and hard of hearing (DHH) on the student's progress
- requesting additional time to work with the student on reading goals during free-choice time and when the student has completed other academic assignments during the school day
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because when a student is not making progress toward Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals in areas in which they also work with a specialist, the special education teacher should first meet with that specialist to ensure they are taking all necessary steps to support the student according to their IEP. There may be other ways the student's accommodations should be applied, other information the specialist could provide, or other interventions or supports they could recommend to support the student in accessing the academic curriculum. Option A is incorrect because the special education teacher should not provide students with additional assistive technology without meeting with the student's specialist, in this case teacher of the deaf and hard of hearing (DHH), and the student's ARD committee. A student's assistive technology is included in their IEP and if additional assistive technology is requested, it should be made through the ARD committee. Option C is incorrect because even though parents/guardians know their children best, it is the special education teacher and the teacher of the deaf and hard of hearing (DHH) who are trained in observing the student's reading progress. Option D is incorrect because if the student has free-choice time during the school day, it is important that they are able to use the time for that purpose. Students should not have IEP goals that require them to spend excessive amounts of time on specific academic tasks.
18. An eighth-grade student is receiving special education services for autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The student has demonstrated the following strengths and needs.
Strengths
- logical thinking ability
- structured rule follower
- strong memory
- precise and detail oriented
Needs
- resistance to change in routines
- anxiety about transitions
- avoidance of unpleasant tasks
- confusion caused by multisensory inputs
The Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee is meeting to determine the least restrictive environment (LRE) for delivering educational services to the student. When considering the provision for supplementary behavioral support services, during which of the following circumstances should the ARD committee consider delivering these supplementary aids and services in alternative placements?
- when the student would prefer to receive the services in an alternative setting
- when high-quality special education classroom settings are available for use
- when the services cannot be delivered satisfactorily in the general education classroom setting
- when a paraprofessional is unavailable for one-on-one support in the classroom setting
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because least restrictive environment (LRE) is a component of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), which is a federal law. LRE states that to the maximum extent appropriate, students with disabilities should be educated with students who do not have disabilities and that students with disabilities should be educated outside of the general education environment only if the nature or severity of the disability is such that education in general education classes with the use of supplementary aids and services cannot be achieved as well as is needed. Option A is incorrect because although the student's input about their own education is important, the law requires that they are educated in general education classes as much as possible. Option B is incorrect because the only time the student should receive education in a special education classroom is when it is required in their Individualized Education Program (IEP) or when they cannot receive services adequately in the general education classroom, not because a high-quality special education classroom is available. Option D is incorrect because the question does not mention that the student works with a paraprofessional; if the student did work with one, it would need to be determined that they would not receive services satisfactorily in the general education classroom without the paraprofessional for them to receive services in an alternative placement.
19. A seventh-grade student with a genetic developmental disorder receives special education services for an intellectual disability (ID). The student has recently returned to the school campus from a residential facility. The student is struggling with behaviors at home that have been leading to difficulties each morning upon arrival at school for the past four weeks. The special education teacher has collected data from the student's teachers and parents/guardians and has determined that the parents/guardians need support with the student's morning routines including supporting the student's hygiene, dressing, and breakfast. These activities are causing power struggles between the student and the parents/guardians at home and lead to disruptive and noncompliant behaviors during the first through the third class periods at school most days. The special education teacher briefly summarizes the data collected about the student.
Ignored instructions: 13 of 20 days
Delayed starting assignment: 12 of 20 days
Disturbed independent work time by talking: 14 of 20 days
Other noncompliant behavior: 17 of 20 days
Which of the following actions should the special education teacher take next to best promote the student's success in their least restrictive environment (LRE)?
- meeting with a behavior specialist, a licensed specialist in school psychology (LSSP), representatives from a local mental health agency, and the student's parents/guardians to consider noneducational community-based support services funding for families supporting a child with a disability at home
- scheduling a meeting with the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee and including the district's special education director to consider the student attending the residential facility part-time for continued therapy around morning routines
- arranging a meeting with the student and a paraprofessional to develop ideas and strategies (e.g., behavior chart, reward system, scheduled movement breaks) to assist the student in developing improved behavior at school
- continuing to collect data about the student's behaviors at the beginning of the school day to share with parents/guardians at the next annual Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting and encouraging the parents/guardians to develop improved strategies for their family's morning routine now that their child has returned from the residential facility
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the behavior specialist, licensed specialist in school psychology (LSSP), representatives from a local mental health agency, and the student's parents/guardians are the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee members that have the knowledge and skills necessary to consider the most appropriate non-educational community-based support services that would support the student's social-emotional and behavioral needs. The student and the parents/guardians are likely to benefit from non-educational community-based support services, such as attendant care, individual and family support, and family dynamics training. Option B is incorrect because it would be inappropriate to suggest a more restrictive educational placement before attempting behavioral intervention both at school and at home to support the student's needs. Option C is incorrect because the student requires comprehensive behavioral support at home and school and although the paraprofessional and student could develop ideas and strategies, it is necessary to create a comprehensive plan with a wider range of professionals with whom the student works to facilitate improved student behavior at school. Option D is incorrect because continuing to collect data and encouraging the parents/guardians to implement strategies to improve their morning routine would not effectively support the student's behavioral needs at school or home. The parents/guardians require professional support services to promote positive change in the home environment and this change, along with a coordinated plan, is likely to influence the student's behavior at school.
Competency 009—(Professional Learning and Responsibilities): Apply knowledge of the professional roles and responsibilities of the early childhood–grade 12 special education teacher.
20. A third-grade special education teacher and a third-grade general education teacher work with students who need varying levels of support. They discuss planning considerations to advocate for optimal educational outcomes for each student. Which of the following approaches would be most effective for the special education teacher and the third-grade teacher to take to meet this goal?
- determining that the special education teacher should take responsibility for instruction for students with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and report progress to the general education teacher regularly
- obtaining informational materials and videos about commonly used instructional and grouping strategies to support Individualized Education Program (IEP) goal progress monitoring
- designing grading criteria for students in the class based on their present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) and Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals
- requesting input and feedback from students and their parents/guardians throughout the development and implementation of students' Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and other instruction
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because obtaining continuous input and feedback from students and their parents/guardians would best inform the general education teacher and the special education teacher about the effectiveness of the individualized instruction they are providing to the student. Feedback and input would provide valuable information to objectively evaluate the efficacy of the strategies and approaches they have implemented. To provide optimal educational outcomes to students, it is important to seek student and parent/guardian input and feedback. The teachers can then adapt, modify, or continue with the strategies and approaches they are using based on feedback they receive. Option A is incorrect because both the general education teacher and special education teacher are responsible for the education of students with a disability who are placed in the general education setting. Option B is incorrect because obtaining informational materials and videos about commonly used instructional and grouping strategies would promote the knowledge and skills of the teachers, but this information is general and is not the most effective approach for promoting the optimal educational outcomes for an individual student's strengths and needs. Option C is incorrect because PLAAFPs and IEP goals are not used to design grading criteria.
21. A fourth-grade student receiving special education services for a specific learning disability (SLD) in basic reading and reading fluency makes considerable advances academically during the spring semester. The student's special education teacher thinks that several changes should be made to the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) annual goals to continue the student's academic progress. The school notifies the parents/guardians of their child's upcoming annual Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting. The parents/guardians return the signed notice indicating they consent to the ARD committee meeting and will be unable to attend but want to be made aware of the results of the meeting. Which of the following actions should the special education teacher take first to inform the student's parents/guardians of the meeting outcomes?
- telling the parents/guardians that an additional ARD committee meeting will be held when they are able to attend to finalize the student's updated IEP goals
- providing the updated IEP to the parents/guardians and asking them if they have any questions or concerns about the new or existing content
- asking the parents/guardians how they would like their child's updated IEP goals progress monitored by the special education teacher
- inviting the parents/guardians to upcoming workshops in the community about the student's SLD and IEP goals and recommending that they attend
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the special education teacher should communicate the outcomes of the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting to encourage input from the parents/guardians. By providing the parents/guardians with a copy of their child's updated Individualized Education Program (IEP), the parents/guardians have the necessary information to ask focused questions and to inquire about specific aspects of their child's education. Option A is incorrect because even though the parents/guardians have the right to participate in meetings and should be encouraged to do so, an additional ARD committee meeting does not need to be held based on the response provided by the parents/guardians on the meeting notice. Option C is incorrect because it would be inappropriate for the special education teacher to ask parents/guardians how they would like their child's progress to be monitored as this would best be determined by the special education teacher. Option D is incorrect because the special education teacher should communicate the outcomes of the ARD committee meeting before inviting the parents/guardians to a workshop about their child's specific learning disability (SLD).
Clustered Questions
Use the information below to answer the two questions that follow.
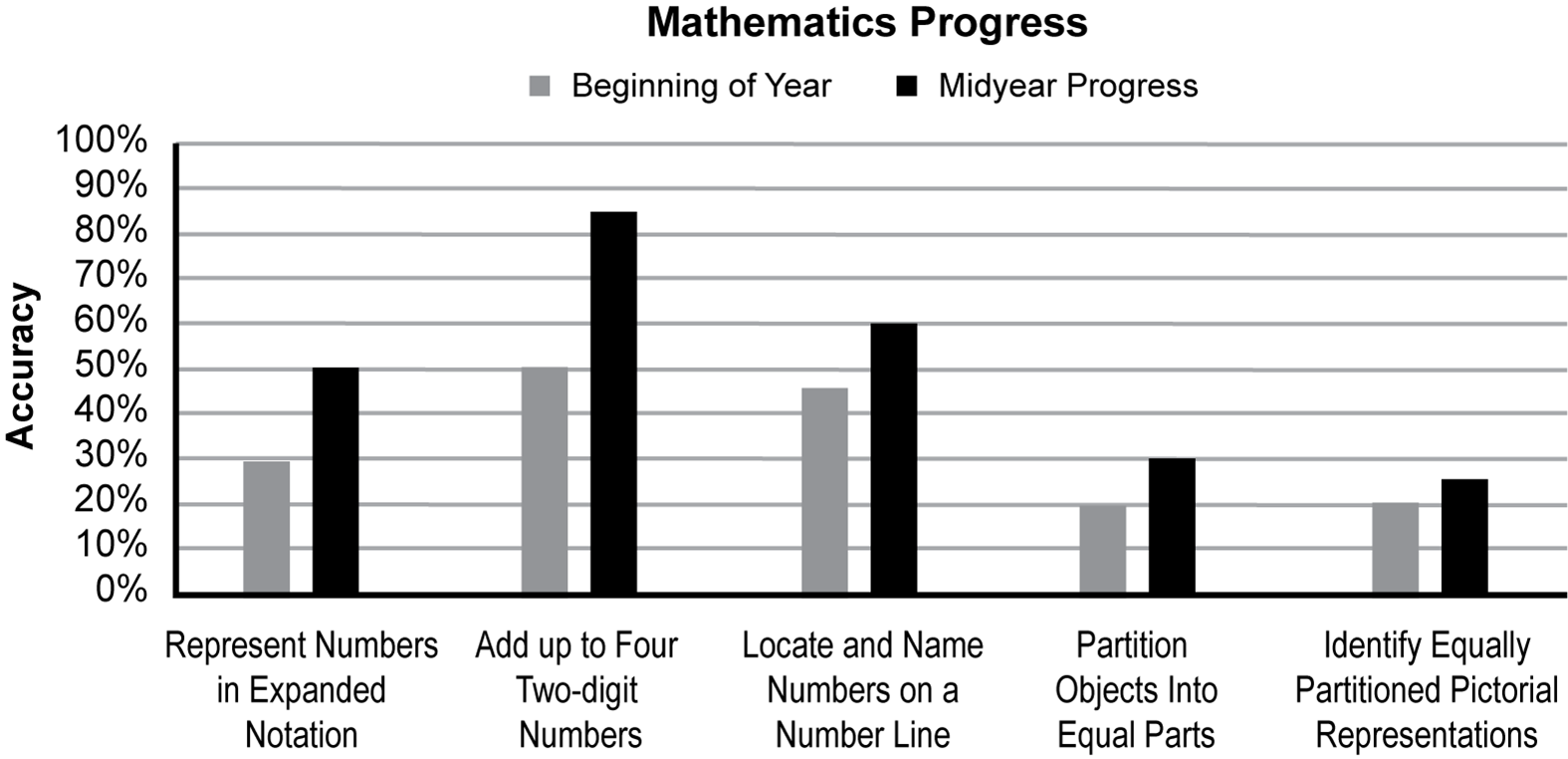
A special education teacher works with a fourth-grade student with a specific learning disability (SLD) in mathematics calculation. The student worked on the following Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals during the last IEP period.
1. By the next IEP, during written mathematics calculation activities, the student will represent a number up to 100,000 using expanded notation in eight out of ten opportunities.
2. By the next IEP, during written mathematics calculation activities, the student will add up to four two-digit numbers correctly in eight out of ten opportunities.
3. By the next IEP, when working with numbers on a number line, the student will locate the position of a given whole number and name the whole number that corresponds to a specific point on a number line in eight out of ten opportunities.
4. By the next IEP, when working on pictorial representations of fractions using circles, squares, or other shapes, the student will partition the shapes into equal parts with denominators of 2, 4, and 8 in eight out of ten opportunities.
5. By the next IEP, when reviewing pictorial representations of fractions, the student will identify the equal partitions representing fractions with denominators of 2, 4, and 8 in eight out of ten opportunities.
The special education teacher collects the following data on the student's progress.
The bar graph measures two variables, beginning of year and midyear progress. The skills that are measured are represent numbers in expanded notation, add up to four two-digit numbers, locate and name numbers on a number line, partition objects into equal parts, and identify equally partitioned pictorial representations. In representing numbers in expanded notation, the student achieved 30% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 50% accuracy midyear. In adding up to four two-digit numbers, the student achieved 50% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 85% accuracy midyear. In locating and naming numbers on a number line, the student achieved 45% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 60% accuracy midyear. In partitioning objects into equal parts, the student achieved 20% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 30% accuracy midyear. In identifying equally partitioned pictorial representations, the student achieved 20% accuracy at the beginning of the year and 25% accuracy midyear.
State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) Results—Grade 3 Subject Area Score Result Reading 1500 Meets Grade Level Mathematics 825 Did Not Meet Grade Level
Competency 003—(Assessment for Data-Driven Decision Making): Apply knowledge of the evaluation and assessment process and of appropriate assessment strategies to inform instructional design and to support students.
22. The special education teacher can most effectively use the results of the student's scores on the State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) exam to:
- determine if IEP goals correspond with STAAR mathematical assessment targets.
- provide a benchmark of the success of program modifications and supports used to address each IEP goal.
- supplement progress monitoring data related to each IEP goal with information about state-required knowledge and skills data.
- track the student's progress toward meeting each IEP goal by the end of the school year.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the purpose of the State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) test is to determine a student's mastery of grade-level state curriculum standards in the core subjects (e.g., reading, writing, mathematics, science, social studies). Although STAAR results do not directly measure progress toward Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals, the results can be used alongside discrete progress monitoring data to demonstrate the student's acquisition of knowledge and skills. Option A is incorrect because the STAAR test measures progress toward state curriculum standards in the core subjects, including mathematics, and depending on the needs of the student, these assessment areas may not directly align with the IEP goals. Given that the student's STAAR test mathematics score is a single metric, the special education teacher could not use it to determine if the IEP goals correspond with STAAR assessment targets. Option B is incorrect because the STAAR test is designed to globally measure academic growth and readiness for the next grade, not to provide benchmark data about progress toward individual IEP goals. Option D is incorrect because the STAAR test is not designed to track progress toward IEP goals but to provide a global measure of a student's annual learning growth in the core subject areas.
23. The special education teacher plans to share the data with the student's parents/guardians at an upcoming Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting. The parents/guardians are emergent bilingual and understand conversational English. Which of the following steps will best ensure that the parents/guardians have the opportunity to fully participate in the ARD committee meeting?
- providing the data to the parents/guardians in their home language and requesting a translator attend the meeting to communicate with the parents/guardians
- mailing the data to the parents/guardians ahead of the meeting so they have time to review it and to generate questions for the ARD committee
- collaborating with the English as a Second Language (ESL) specialist and asking them to lead the ARD committee meeting
- recording any questions the parents/guardians have at the end of the meeting and sharing them with a translator to provide responses to the parents/guardians
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the parents/guardians have a right to access their child's progress monitoring data and State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) results documents, and to have the ARD committee meeting held in their preferred language. Option B is incorrect because even if the data are mailed ahead of the ARD committee meeting, it is unlikely that the parents/guardians can fully access the information about their child if it is not presented in their preferred language. Option C is incorrect because the English as a Second Language (ESL) specialist may not speak the home language of the parents/guardians, and it would be inappropriate for the ESL specialist to lead the ARD committee meeting. Option D is incorrect because recording the questions of the parents/guardians for a translator to respond to would not support parent/guardian participation in the ARD committee meeting. This approach would minimize the participation of the parents/guardians and could lead to incorrect information given that the translator, not the committee members, would be responding to their questions.
Use the information below to answer the two questions that follow.
A twelfth-grade student who will turn 18 during the school year receives special education services for an intellectual disability (ID) eligibility. The student plans to participate in their annual Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting. The meeting agenda is shown below.
Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) Committee Meeting Agenda
- Introductions
- Purpose of ARD Committee
- Statement of Confidentiality and Meeting Norms
- Review of Existing Evaluation Data (REED)
- Determination of Eligibility
- Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP)
- Development of Accommodations
- Determination of and Participation in Assessments
- Consideration of Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
- Determination of Services
- Reading of Assurances
- Signatures
Competency 001—(Legal and Ethical Guidelines): Apply knowledge of applicable state and federal laws and procedures that pertain to special education services.
24. The ARD committee is at the part of the meeting in which they discuss the student's PLAAFP. Which of the following actions would take place at this point in the meeting?
- determining the student's special education eligibility and educational services category
- evaluating the student's formal and informal assessment results
- discussing the student's strengths and critical needs
- identifying supports to be provided as a part of the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP)
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the present levels of academic achievement and functional performance (PLAAFP) is a section of the Individualized Education Program (IEP) summarizing the student's current level of functioning both academically and functionally. This section of the IEP would contain information about the student's current levels of performance, learning strengths and needs, and a description of how disability affects the student's access to the general curriculum. Option A is incorrect because the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee would not determine the student's special education eligibility and educational services category when discussing the PLAAFP. The student's eligibility and educational services category would be determined during the Determination of Eligibility section of the ARD meeting. Option B is incorrect because evaluating the student's formal and informal assessment results would occur during the Review of Existing Evaluation Data (REED) section, not the PLAAFP section of the ARD meeting. Option D is incorrect because identifying supports to be provided as part of the student's IEP would be determined during the Determination of Services section, not the PLAAFP section of the ARD committee meeting.
25. The student would like to attend all general education classes during their senior year. During which of the following portions of the ARD committee meeting should the student discuss this with the ARD committee?
- VII. Development of Accommodations
- IX. Consideration of Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
- X. Determination of Services
- XI. Reading of Assurances
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee members, including the student, would discuss placement in the general education setting during the Consideration of Least Restrictive Environment (LRE) section of the meeting. Option A is incorrect because during the Development of Accommodations section of the ARD committee meeting, committee members would identify the accommodations that are necessary to promote the student's access to learning. Option C is incorrect because during the Determination of Services section of the ARD committee meeting, the committee members would determine which special educational services, including related services, are necessary to support the student's educational needs. Option D is incorrect because during the Reading of Assurances section of the ARD committee meeting, committee members objectively review the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) to assure that the student is educated alongside peers without disabilities to the maximum extent appropriate.
Additional Selected-Response Questions
This section includes additional sample selected-response questions for you to review in preparation for the exam. The correct answer is provided for each question below.
Domain I—Legal and Ethical Guidelines and Knowledge of Learners
Competency 001—(Legal and Ethical Guidelines): Apply knowledge of applicable state and federal laws and procedures that pertain to special education services.
26. A Full and Individual Initial Evaluation (FIIE) has been conducted for a third-grade student referred for special education services. The evaluation results show that the student is performing significantly below their grade-level peers in mathematics problem solving. To indicate that the student qualifies for special education as a student with a specific learning disability (SLD) in mathematics problem solving, the student's evaluation must also show that they:
- demonstrate strengths in mathematics calculation.
- would benefit from small-group or one-on-one intensive instruction.
- are not making significant progress after completing Tier 3 interventions.
- have received Tier 2 interventions for a minimum of 20 weeks.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
27. A new first-grade teacher asks the special education teacher why a new student in the class needs a Full and Individual Initial Evaluation (FIIE) even though a doctor has provided a note indicating that the student has been diagnosed with diabetes. Which of the following responses from the special education teacher best answers this question?
- New students may not be identified for special education services without going through the Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS) process.
- Students with diabetes do not fall under a disability category covered by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
- Formal evaluations by law must determine whether the student has a need for special education and related services.
- Public schools do not have to consider evaluation data from professionals who are not associated with educational institutions.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Competency 002—(Knowledge of Learners): Apply knowledge of understanding how to address each student's developmental, communication, and learning needs.
28. A fourth-grade emergent bilingual student is eligible for special education services for a specific learning disability (SLD). Although the student speaks English fluently, the student rarely speaks to teachers or to other students unless they are spoken to first. The student completes all assignments and appears comfortable in their environment but engages with others minimally. Concerned about this behavior, the general education teacher suggests to the special education teacher that the student may need social skills instruction. Which of the following actions should the teacher take first in this situation?
- introducing the student to additional students in their grade and encouraging them to play together at recess and sit together at lunch
- working with the student on social and emotional learning (SEL) activities to promote their self-confidence and their belief in their ability to succeed
- meeting with the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee and requesting an additional Individualized Education Program (IEP) goal promoting the student's social behavior
- developing an observation and data collection plan to progress monitor the student's academic, social, and emotional strengths and needs
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct.
29. A special education teacher and a general education teacher work with a fourth-grade emergent bilingual student who meets criteria for a specific learning disability (SLD) in reading comprehension. Which of the following approaches is most effective for the teachers to use when working with this student on unfamiliar academic content?
- introducing mnemonic devices to improve the student's memorization skills
- allowing the student to dictate their responses to test questions
- pre-teaching vocabulary that is needed for the lesson to the student
- asking the student to listen carefully to class discussions and repeat what they heard
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
30. A special education teacher and a fifth-grade general education teacher create classroom rules with their students at the beginning of the school year. The teachers want to develop classroom rules that are supportive of students with different types of strengths and needs and from a range of cultural and linguistic backgrounds. Which of the following approaches should the teachers take to meet this goal?
- including all students' suggestions and ideas that are productive and accessible to all students in the class
- conveying to students that rules will be consistently enforced to create a secure environment
- deciding on a reward system that will promote students' cooperation with classroom rules
- determining how many rules and how much structure should be encouraged in the classroom based on feedback from students
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
31. A fifth-grade student who is eligible for special education services for a specific learning disability (SLD) in oral expression is gifted in basic reading and reading comprehension. Which of the following instructional strategies should the student's teachers take to support the student's needs most effectively?
- designing instruction for the student that provides targeted intervention in oral expression needs as well as accelerated reading activities
- assigning the student advanced reading and writing assignments that they can complete independently outside of school
- allowing the student to write or type responses to reading comprehension questions instead of answering verbally
- requesting strategies from the gifted and talented teacher to support the student's participation in grade-level reading group circles
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
32. A seventh-grade student who is identified as twice exceptional receives gifted/talented services and special education services for other health impairment (OHI): attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The student exhibits strong critical-thinking and problem-solving skills during a science class experiment. The student is curious about every aspect of the experiment, and the teacher notices that the student is able to concentrate completely during this activity, which contrasts with the student's tendency to get distracted easily during other types of lessons. Which of the following actions should the teacher take in the classroom to support the student?
- changing the focus of the special education support from ADHD scaffolds to problem-solving enrichment
- integrating the elements of experiments that the student enjoys and excels in into other academic tasks
- allowing the student to spend additional time on science experiments and less time on other science activities
- teaching the student how to transfer their interest in science experiments to other academic tasks, such as writing essays
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
Domain II—Assessment and Program Planning
Competency 003—(Assessment for Data-Driven Decision Making): Apply knowledge of the evaluation and assessment process and of appropriate assessment strategies to inform instructional design and to support students.
33. A special education teacher provides a small group of second-grade students with direct instruction in mathematics calculation in accordance with the following Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Grade 2 Mathematics.
(7) Algebraic reasoning. The student applies mathematical process standards to identify and apply number patterns within properties of numbers and operations in order to describe relationships. The student is expected to:
(A) determine whether a number up to 40 is even or odd using pairings of objects to represent the number; and
(B) use an understanding of place value to determine the number that is 10 or 100 more or less than a given number up to 1,200.
After ten minutes of providing instruction, the teacher asks the students two questions requiring short responses on note cards. After quickly reviewing the cards, the teacher returns to instruction. Which of the following types of assessment is the teacher using in this situation?
- formal
- summative
- formative
- alternate
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
34. A special education teacher shows an unfamiliar storybook to a prekindergarten child. The teacher asks the child to point to the title of the book and to open the book to the first page of the story. After the teacher reads a few pages, the teacher asks the child to point to the words, then to a specific word, and then to specific letters within a word. The teacher can most effectively assess the child's understanding of which of the following components of emergent literacy through these actions?
- Print conventions can convey emotion in text.
- Printed text carries meaning.
- Readers can make inferences about text.
- Text includes left-to-right and top-to-bottom directionality.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
35. A special education teacher regularly analyzes the attempted spellings of emergent readers. In addition to providing information about students' spelling development, the teacher's approach would best support the teacher in assessing students':
- use of word-identification strategies.
- level of reading fluency.
- ability to apply phonics skills.
- knowledge of comprehension strategies.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Domain III—Curricular Knowledge and Instructional Practices
Competency 005—(Subject Matter Content and Specialized Instructional Strategies): Apply knowledge of implementing curriculum through relevant and appropriate content and specialized instructional strategies to guide and support students' learning and development.
36. A sixth-grade mathematics general education and special education teacher are co-teaching a mathematics lesson in accordance with the following Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Grade 6 Mathematics.
(3) Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division while solving problems and justifying solutions. The student is expected to:
(D) add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers fluently.
During instruction, a student with a specific learning disability (SLD) in mathematics calculation and problem solving participates in the lesson and is able to correctly answer questions about the concepts. However, the student does not demonstrate mastery during independent practice. The student completes the following work sample.
2 plus negative 3 equals 1 to the negative negative 3 times negative 4 equals 16 7 plus negative 12 equals negative 4 negative 6 plus negative 7 equals negative 12 8 times negative 6 equals negative 46 negative 9 plus negative 6 equals negative 16
Based on this student's work sample from the most recent mixed problem independent practice, which of the following approaches would best support the student in moving toward mastery of this standard from the TEKS?
- additional mathematics fluency homework for practice
- an adaptive mathematics facts fluency program
- shortened mathematics fluency assignments
- activities to support mathematics fluency in the use of operations
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
37. A transition-planning meeting was recently held for a ninth-grade student who receives special education services for multiple disabilities (MD) eligibility, including an intellectual disability (ID), speech language impairment (SLI), and visual impairment (VI). At the meeting, the student and their parents/guardians expressed concerns about the student's future. It is the student's and their parents'/guardians' understanding that the student will need lifelong, ongoing support, and as a result they were not sure how to answer questions during transition planning about the student's employment interests and goals. To best support the student and their parents/guardians during the transition-planning process in understanding the student's employment options, the special education teacher should take which of the following actions?
- focusing on the more immediate education goals and objectives and independent-living skills that can be more easily addressed on campus and leaving the employment goals for later in high school and/or during adult transition services after high school graduation
- recommending that the family look for volunteer options in the community (e.g., public library, animal shelter, homeless shelter) for meaningful ways the student can engage in the community in a way that feels like employment
- encouraging the student and the family to research workplaces in the community that they find interesting and believe would be a good fit for the student and to contact those workplaces to learn about prerequisites for employment
- providing resources to the student and the family about the Texas Workforce Commission (TWC) for employment-related transition services and talking with the student about various supported employment models available in the community that may interest them
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct.
Competency 006—(Supporting Learning Using Effective Instruction): Apply knowledge of diverse strengths and needs of students to plan appropriate, effective, meaningful, and challenging instruction.
38. A second-grade student with a specific learning disability (SLD) in basic reading demonstrates difficulty blending sounds into words and with identification of consonant digraphs, short vowels, long vowels, and final sounds. The student enjoys when the teacher conducts read-alouds. The student is able to retell stories accurately and can identify story elements such as main characters, setting, conflict, and resolution. Based on this information, which of the following accommodations would best support the student's comprehension of what they have read?
- text-to-speech assistive technology with a hover speech option that reads digital text to the student
- a graphic organizer to promote the student's understanding of literary elements
- highlighter markers and sticky notes to identify key points and vocabulary in a story
- a speech-generating device that plays prerecorded words or phrases when the student presses a corresponding button or key with a picture of the word or phrase
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
39. A third-grade general education teacher and a special education teacher are planning a personal narrative unit for the following week, in accordance with the following Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Grade 3 English Language Arts and Reading (ELAR).
b. Knowledge and skills
(12) Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts–genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful. The student is expected to:
(A) compose literary texts, including personal narratives and poetry, using genre characteristics and craft.
As a performance task, each student will write a one-page story about something that has happened in their life. One student in the class has attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and has organizational support written in as an accommodation into their Individualized Education Program (IEP). Which of the following strategies would best support the student in completing the performance task?
- teaching the student to make and use a "to do" checklist from the written directions
- providing the student with a keyboard for typing
- allowing the student to use scratch paper for note taking
- creating an outline for the student to use when writing their first draft
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
40. A ninth-grade student who receives special education services for other health impairment (OHI): attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and an emotional disturbance (ED) has difficulty engaging in classwork during English I assignments and activities. The English I teacher usually presents an interactive lesson or activity at the beginning of class, then gives students a written assignment to work on individually or in assigned pairs at their desks for the duration of class. The student is often engaged during the interactive portion of class. During independent work time, the student frequently begins talking to peers and teachers about topics unrelated to the assignment or singing and fidgeting with pencils and other materials. The English I teacher and the special education teacher notice that the student is having difficulty completing their work. The special education teacher recommends suggestions to support the student's development of sustained engagement during assignments. Which of the following approaches would be most effective in supporting this goal?
- developing self-regulatory goals with the student and teaching the student to use reminders and checklists to increase the duration of their on-task behaviors
- providing the student with extra movement breaks outside of the English I classroom
- assigning a classmate to work on all written English I assignments with the student
- seating the student at the front of the classroom and encouraging them to request one-on-one support from teachers during independent work time
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
Competency 007—(Supporting Social, Behavioral, and Emotional Growth): Apply knowledge of strategies to create effective and safe learning environments, methods to promote students' positive behavior, and supports to develop and measure behavioral interventions.
41. A special education teacher and a prekindergarten teacher co-teach a prekindergarten class. The teachers observe that a child in the class receiving special education services with a Non-Categorical Early Childhood (NCEC) eligibility enjoys school but has difficulty following classroom expectations and schedules. The child arrives each day and immediately runs toward whichever area of the classroom attracts their interest, and continues running throughout the classroom for ten to fifteen minutes, stopping briefly in various areas before settling in to an activity. Which of the following actions should the teachers take first to support the student's integration to the classroom each day?
- meeting with the child's parents/guardians to discuss their behavior expectations at home and adding these contributions to classroom expectations
- providing the child with an individualized behavior checklist on their cubby to remind them of their behavior goals
- creating a reward system to implement when the child follows the classroom rules the teachers have created
- individualizing the child's arrival routine to include supported exploration of the classroom with a teacher, and practicing whole-class routines with the child after their initial exploration
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct.
42. A sixth-grade student receives special education services for an emotional disturbance (ED) eligibility after having been diagnosed with an anxiety disorder by a physician. The student has grade-level mathematics problem-solving and number-operations skills. The student's anxiety most frequently occurs when the student perceives uncertainty such as during transitions from one activity to another and when working in collaborative groups to complete multistep performance tasks that do not have one correct answer. The student is working toward the following Individualized Education Program (IEP) goal.
By the next annual IEP, in a collaborative skills practice situation, the student will use coping strategies to remain calm during challenging learning activities in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
The special education teacher who co-teaches the student's mathematics class uses visual cues to help the student prepare for new activities with lessened anxiety and provides the student with an agenda for the class period. In one class, the teacher divides the class into small groups and assigns each group a problem-solving performance task to complete. Given the information about the student, which of the following scaffolds would best support the student in successfully interacting socially and completing the task with the group and meeting the IEP goal?
- breaking the performance task into steps and providing a rubric for performance task expectations
- giving the group extended time to complete the performance task
- allowing the student to choose individual responsibilities within the group first
- pairing the student with a partner instead of assigning them to a larger group to complete the assignment
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
43. A special education teacher works with a twelfth-grade student who receives special education services for an emotional disturbance (ED). A functional behavioral assessment (FBA) concluded the following information about the student.
1. The student initiates disruptive social interactions when the teacher is giving another student attention.
2. The student initiates varying disruptive behaviors to postpone or avoid disliked tasks.
As a result of the conclusions, the student has a behavioral intervention plan (BIP) as part of their Individualized Education Program (IEP). As part of the BIP, the special education teacher works with the student, providing explicit instruction to replace disruptive behaviors with effective approaches to gain the teacher's attention and begin challenging tasks. Which of the following methods should be used to monitor the effectiveness of the behavioral interventions?
- asking the student to self-report when and how the behavioral interventions are being used in each of their classes
- interviewing the student's teachers about how they have observed the student behaving during class using a targeted behavior questionnaire
- providing the student's teachers with an anecdotal recording form to complete and instructing them in how to use it with the student each week
- assigning a paraprofessional to make periodic observations of the student and note uses of and responses to behavioral interventions
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Domain IV—Professional Collaboration, Learning, and Responsibilities
Competency 008—(Consultation and Collaboration): Apply knowledge of strategies, approaches, and techniques for effective consultation and collaboration with students, parents/guardians, school personnel, and other professionals to support students' development and learning.
44. A special education teacher and related service specialists apply a multidisciplinary approach when working with an eleventh-grade student with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The student attends general education classes and receives services from the special education teacher, a speech language pathologist (SLP), and the licensed specialist in school psychology (LSSP). A multidisciplinary approach is beneficial in this situation because it allows the special education teacher and the related service specialists to:
- deliver assessments and instruction to the student independent of other services to ensure efficient delivery.
- integrate the expertise of all team members so more comprehensive assessment and intervention services may be provided to the student.
- share results of interventions and assessments they have conducted with the student while each continuing their own individual programs with the student.
- conduct assessments simultaneously and develop intervention programs for the student's parents/guardians to implement at home.
- Answer
- Option B is correct.
Competency 009—(Professional Learning and Responsibilities): Apply knowledge of the professional roles and responsibilities of the early childhood–grade 12 special education teacher.
45. A special education teacher is working with a first-grade student with an orthopedic impairment (OI) that affects fine- and gross-motor skills. Which of the following statements best describes the roles of teachers and service providers who work with the student?
- The special education teacher should advise the general education teacher and other service providers on how to provide effective instruction for the student.
- The teachers and service providers should collaborate to provide common accommodations across settings to support the student's learning, such as wide classroom aisles, pencil grips, and reduced writing tasks.
- The special education teacher should write lesson plans and Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals for the general education teacher and service providers to use with the student.
- Each teacher and service provider should write goals to be used exclusively in their therapeutic setting.
- Answer
- Option B is correct.
46. A sixth-grade student who is eligible for special education services for a visual impairment (VI) with a visual processing disorder has failed the last two unit tests in science class. The special education teacher has provided opportunities for reteaching concepts, copies of study guides, and test-taking strategies. The student also has testing accommodations written into their Individualized Education Program (IEP) that include oral accommodations and extended time. After noticing that the student has become withdrawn, sitting at the back of the classroom with their head down during lectures, the special education teacher engages the student in the following conversation.
Teacher: I notice that you haven't been participating in class discussions lately.
Student: Yeah, it doesn't seem to matter if I pay attention. I can't seem to pass a test.
Teacher: That must be very frustrating.
Student: It is! When I review with you, I feel like I know all the material, but every time I take the multiple-choice test, I feel like the correct answer isn't there.
Teacher: I agree that you know the concepts during our study sessions.
Which of the following steps taken by the special education teacher would be most effective in improving the testing outcome for the student?
- asking the general education teacher to call on the student during the lecture to increase engagement time
- enrolling the student in a study skills class to learn additional test-taking strategies
- referring the student to the counselor to develop stress management techniques
- collaborating with the general education teacher and teacher of students with visual impairments (TVI) to develop alternative forms of assessment such as oral response or presentations
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
47. A ninth-grade special education teacher has participated in a Teacher Goal-Setting and Professional Development (GSPD) process throughout the school year. As a part of the process, the teacher gathers data to meet with their mentor in an end-of-year conference to reflect on progress, celebrate success, note lessons learned, and look toward the subsequent year's goals for development. The teacher's goal and their method of monitoring their progress are shown below.
Goal: Develop and execute lessons that employ a gradual release of responsibility model for learning.
Monitoring: Identified lessons/units that meet goal, tracked implementation, and asked for student reflections.
In preparation for the meeting, the teacher notices a discrepancy between the students' reflections on the lessons and the teacher's journal tracking of their implementation strategies. Which of the following actions should the teacher take to reconcile the differences?
- researching alternative monitoring tools to use in the subsequent year that better gather data
- meeting with the general education teacher to confirm the lessons developed to meet the goal include strategies for gradual release
- analyzing the tracking journal to identify lessons in which the gradual release model was not followed
- cross-referencing the implementation strategies used with the student reflections to look for patterns
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
48. A special education teacher provides services to a tenth-grade student receiving special education services. The special education teacher is preparing for the student's annual Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting. The teacher reviews the student's documentation and observes that the student has not yet attended an ARD committee meeting. Which of the following actions should the special education teacher take next?
- meeting with the student's general education teachers and school counselor to discuss the student's potential involvement at the upcoming ARD committee meeting and asking them for suggestions for a successful meeting
- asking the student if they would like to attend their next ARD committee meeting and letting them know when it will be held
- requesting consent from the parents/guardians for the student to attend the ARD committee meeting
- talking with the student and their parents/guardians about the importance of the student being at the ARD committee meeting and practicing with them what to expect at the meeting and how to participate
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
Clustered Questions
Use the information below to answer the two questions that follow.
A five-year-old kindergarten student who has recently moved to the school district attends a general education class. The class is co-taught by a general education teacher and a special education teacher. The student demonstrates difficulty participating effectively and transitioning between academic and social activities in the classroom. The teachers have engaged the student in Tier 1 and Tier 2 interventions such as small-group instruction to support the student in the classroom during the weeks the student has been present. The special education teacher collects data on the student at various times during the day. An excerpt of data the special education teacher has collected is shown in the antecedent-behavior-consequence (A-B-C) chart below.
Date and Time/ Activity Antecedent Behavior Consequence September 10, 8:50 a.m.
Learning CentersThe student was working on a mathematics learning center activity. After five minutes, the teacher asked students to clean up and transition to the group reading activity on the rug. The student continued to participate in the mathematics learning center activity after the rest of the class had finished learning centers and gathered for the reading activity. The student ignored the teacher's request and continued the mathematics activity. A paraprofessional sat at the learning center with the student while the classroom teacher began the reading activity. September 12, 1:15 p.m.
Small-Group Science ActivityThe group observed a classroom terrarium using magnifying glasses, pencils, and their science journals. A classmate requested to borrow the student's magnifying glass. The student yelled, "No, this is mine!" and pushed the classmate's journal onto the floor. The classroom teacher requested that the student apologize to the classmate and pick up the journal and pencil from the floor. The student refused and sat in a chair in the reading corner of the classroom. September 14, 8:50 a.m.
Learning CentersThe student worked in a mathematics learning center. The teacher provided students with reminders to clean up and come to the rug for reading. The student refused to engage, yelling, "I am only doing this activity! Not reading! No, no, no!" The paraprofessional asked the student to take a walk in the hallway. The student refused. The classroom teacher called the school counselor to talk to the student. September 17, 10:30 a.m.
Social Skill GroupThe student participated in a small group with the special education teacher playing with blocks and plastic people. The teacher asked the students to share the blocks to build a town together. The student built their own structure with blocks and animals and said, "I don't want to be part of that group. I want my own little town." The teacher continued to encourage the students in the group to build a town together and modeled asking other students for a block and offering blocks to others.
Competency 001—(Legal and Ethical Guidelines): Apply knowledge of applicable state and federal laws and procedures that pertain to special education services.
49. The student's parents/guardians have told the special education teacher they believe their child has unidentified learning needs. Which of the following actions best describes the special education teacher's first responsibility according to the federal mandate for Child Find in this situation?
- holding an Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee meeting at a time and place that is available to all committee members
- providing the student's parents/guardians with Prior Written Notice for evaluation
- giving the student's parents/guardians the Parent's Guide to the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) Process
- referring the student for a Full and Individual Initial Evaluation (FIIE) and providing the student's parents/guardians with information about special education services on campus
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
Competency 008—(Consultation and Collaboration): Apply knowledge of strategies, approaches, and techniques for effective consultation and collaboration with students, parents/guardians, school personnel, and other professionals to support students' development and learning.
50. The special education teacher, the general education teacher, and the paraprofessional meet to discuss how best to support the student in the classroom. Which of the following approaches would be most effective for the special education teacher to take in this situation?
- recommending that the paraprofessional work with the student in the mathematics learning center each morning
- practicing various positive behavioral intervention strategies with the paraprofessional to implement with the student during transition activities
- suggesting that the paraprofessional work on instructional activities with the student's peers while the special education teacher focuses on the student
- asking the paraprofessional to talk with the student about the importance of listening to the teacher and cooperating in the classroom
- Answer
- Option B is correct.