Section 4: Sample Selected-Response Questions Deafblind EC–12 (185)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for you to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied by the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements do not appear on the actual exam.
The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will see on the exam; however, your performance on the sample questions should not be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual exam.
Selected-Response Questions with Rationales
Each sample exam question here includes the correct answer and a rationale for each answer option.
Domain I—Knowledge of Learners and the Visual, Auditory, Tactile, and Sensory Systems
Competency 001—(Foundations): Apply knowledge of key philosophical, historical, and legal foundations in the education of learners who are deafblind.
1. A student has a bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, colobomas of the eye, and atresia of the choanae. These conditions are typically associated with:
- Waardenburg syndrome.
- CHARGE syndrome.
- Usher syndrome Type 2.
- Williams syndrome.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because CHARGE syndrome is a genetic condition characterized by: coloboma, heart defects, atresial choanae, restricted growth, and genital and ear abnormalities. The student is noted to have three of the six characteristics, which together would most likely indicate CHARGE syndrome. Option A is incorrect because while Waardenburg syndrome can cause hearing loss, this hereditary condition involves changes in skin pigmentation. Option C is incorrect because Usher syndrome Type 2 is typically characterized by a sensorineural hearing loss along with retinitis pigmentosa. Option D is incorrect because Williams syndrome is typically characterized by developmental delay and heart disease.
2. The parents/guardians of a student who is deafblind ask for assistance with paying for intervener services outside of the school day. Which of the following resources would be the most appropriate for the TDB to recommend?
- Deaf Blind with Multiple Disabilities (DBMD) waiver
- Texas Health and Human Services (HHS) Blind Children's Vocational Discovery and Development Program (BCVDDP)
- Texas Workforce Commission Vocational Rehabilitation Services
- Texas Health and Human Services (HHS) Home and Community-based Services (HCS) waiver
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the DBMD waiver provides home and community-based services to people who are deafblind with multiple disabilities. The program focuses on increasing opportunities for individuals who are deafblind with multiple disabilities to communicate and interact with their environment, which an intervener would support. Options B and C are incorrect because these Texas organizations primarily provide vocational services for individuals with disabilities. Option D is incorrect because the Texas HCS waiver program provides services for individuals with intellectual disabilities or related conditions, and intervener services are not one of the approved consumer-directed services in this program.
3. The use of tactile communication systems (e.g., braille, Protactile Language [PTL], Print on Palm [POP]) to promote communication, learning, and access for individuals who are deafblind is supported by which of the following key research findings?
- Studies of brain neuroplasticity indicate increased stimulation of the cortical areas of the brain associated with language development by tactile communication systems.
- Evidence that promotes the theory of multisensory learning modalities includes strategies of tactile communication.
- Student self-perception studies suggest increased enjoyment of learning using tactile communication systems.
- Studies indicate tactile skills reinforce the development of secondary modes of communication and support cognitive development for students with sensory disabilities.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because similar patterns of brain activation are seen in users of braille, Print on Palm, and PTL. Research has shown that the neural networks associated with tactile communication systems are consistent with those implicated with language. Option B is incorrect because multisensory learning focuses on the benefits of learning through more than one sense and integration of the tactile sense with visual, auditory, and kinesthetic activities. Options C and D are incorrect because while tactile learning methods can help improve concentration and increase self-confidence, these are not the key findings within the research.
Competency 002—(Learners' Strengths and Needs): Apply knowledge of the complex and unique effects of combined vision and hearing impairment as well as the strengths of the tactile sense of learners who are deafblind.
4. In a life skills classroom, a second-grade teacher begins a social studies unit about community helpers. The teacher plans individualized instruction for a student who is congenitally deafblind and primarily uses their tactile sense to access their environment. Which of the following approaches would be most effective for supporting the student's concept development when beginning the unit on community helpers?
- reading aloud to the class a picture book about firefighters, police officers, doctors, and teachers and their roles within the community
- creating an experience book with the student about a doctor's visit and providing objects such as the stethoscope, gloves, and tongue depressor for the student to explore
- working with the student using a hand-under-hand approach to color in a picture of community helpers
- providing center activities for the student to explore, such as sorting small plastic fire trucks, police cars, school buses, and ambulances into labeled containers
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because incorporating real objects from an activity in which the student has participated can help connect to their background knowledge as they begin the unit. The student's experience at the doctor's office can be used to build upon as the unit on community helpers progresses. Option A is incorrect because a read aloud is not an interactive or tactile activity for a student who primarily uses their tactile sense. Options C and D are incorrect because coloring and sorting activities do not support initial development of the concept of community helpers.
5. An eight-year-old student who is deafblind with emerging language works on a tactile task while sitting on the carpet. The student picks up different sized blocks and passes them back and forth, hand-to-hand, finally matching them with their corresponding container. Which of the following actions by the teacher is most appropriate to initiate an interaction with the student that is sensory attuned to build trust as the student works on this task?
- sitting at a nearby table, taking notes, and carefully observing the student's movements and actions before actively engaging with the student on the activity they are doing
- picking up each of the blocks one at a time and stacking them on top of each other to build a tower for the student to knock down
- asking the student for a turn with one of the blocks using tactile signs, imitating the student's actions with the block, and putting the block back into the student's hands when done
- sitting with knees touching the student's knees and lightly resting their hands on the student's hands to show they are watching and engaging in the activity as directed by the student
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because the teacher is establishing joint tactile attention. By maintaining contact with the student's knees and hands, the teacher is sharing in the activity through non-controlling mutual touch. Option A is incorrect because observing from a distance does not allow the student to know the teacher is engaged with them. Option B is incorrect because stacking the blocks for the student does not allow the student to direct the activity. Option C is incorrect because imitating the student without maintaining joint tactile attention will not keep the student engaged.
6. A TDB wishes to reference a specific object in the classroom while working with a student who is deafblind. Which of the following actions by the TDB would be the equivalent of using a pointing gesture for communicating with the student?
- taking turns exploring the object the student is touching
- moving with the student toward the object to explore it coactively
- limiting the number of objects near the student and watching what they choose to touch
- imitating what the student does with their hands with a different object
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the teacher establishes and maintains mutual tactile attention. Using coactive engagement encourages focus on and exploration of the target object. Option A is incorrect because taking turns without maintaining contact disrupts tactile communication. Options C and D are incorrect because watching what the student chooses to touch and imitating the student do not allow the teacher to reference a specific object.
Competency 003—(Anatomy/Physiology of the Auditory, Visual, Tactile, and Sensory Systems): Understand the key components and functions of the human auditory, visual, tactile, and sensory systems.
7. A student without the eighth cranial nerve bilaterally displays which of the following types of hearing loss?
- a congenital, profound, and conductive hearing loss
- a congenital, profound, and sensorineural hearing loss
- an acquired, profound, and sensorineural hearing loss
- an acquired, moderate, mixed hearing loss
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because congenital absence of the eighth cranial nerve is associated with a profound sensorineural hearing loss. Option A is incorrect because the eighth cranial nerve is a structure of the inner ear and would not create a conductive hearing loss. Options C and D are incorrect because while the eighth cranial nerve could become damaged through injury, trauma, infection, or other acquired causes, lack of the structure would be due to a congenital cause.
8. Tactile receptors are located primarily in which of the following areas of the body?
- the dermis layers
- hair follicles
- nerve fibers
- subcutaneous tissue
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the dermis layer of the skin contains sensory receptors that allow the body to receive stimulation such as pain, pressure, and temperature. Option B is incorrect because only the nerve endings around a hair follicle can detect hair movement. Option C is incorrect because nerve fibers carry impulses. Option D is incorrect because the subcutaneous layer of skin is the deepest layer made of mostly fat cells and connective tissue.
Domain II—Assessment, Instructional Planning, and the Learning Environment
Competency 004—(Evaluation and Assessment): Apply knowledge of the educational evaluation and assessment process to determine a learner's strengths and needs, and apply appropriate assessment strategies in the learner's preferred mode of communication to support the learner.
9. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A TDB is determining the appropriate accommodations for a student. The student's functional vision evaluation (FVE) results show that the student has a superior field loss to 20° and a need for high contrast. The FVE results also show a difficulty in seeing information presented at distances greater than 3 feet. The learning media assessment (LMA) results show that the student's primary learning channel is visual, and the secondary channel is auditory.
The student uses manual communication but relies on auditory feedback to verify messages. The student prefers using real pictures on the daily calendar of activities rather than cartoons or line drawings. Based on this information gathered from the FVE/LMA, which of the following accommodations would best meet the student's needs and support their independent access to instruction?
- keeping auditory information at a minimum to reduce auditory clutter in the classroom
- providing high-contrast, black-and-white photographs to represent daily activities on the schedule
- pairing auditory information with signed communication and providing visual supports using high-contrast, low-clutter photographs
- alternating between auditory information and signed communication to minimize overwhelming the student
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the student uses manual communication with auditory feedback and prefers real, high-contrast pictures. Pairing auditory information with signed communication supports the student's preferred learning channels and using real pictures with high contrast supports their visual preferences. Options A and D are incorrect because the student uses auditory information as a secondary channel to visual communication and relies on auditory feedback to verify signed messages. Option B is incorrect because while black and white photos are high contrast they do not support the student's preference for real pictures.
10. Standardized assessments can be one of many evaluations administered as part of a communication evaluation. Which of the following concerns regarding the reliability and validity of standardized tests should the TDB be aware of?
- Norm groups for standardized tests often do not include a representative sample of students who are deafblind.
- Standardized tests may not match the classroom instruction received by students who are deafblind.
- Accommodations and modifications may not be available for many standardized tests.
- Any signed interpretation of test items or directions may be transcribed differently in written English on a standardized test.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because standardized tests are designed to compare the performance of one individual to that of a normative group, yet most standardized tests lack adequate norms for students who are deafblind. Without a representative norm group to compare to, results may not be reliable or valid. Option B is incorrect because the purpose of standardized testing does not include matching classroom instruction. Option C is incorrect because there are accommodations that may affect test validity as they may compromise the presentation of the item content or the level of difficulty. While the TDB should be aware of which accommodations and modifications may not be available on standardized assessments, these would not be a primary concern of the TDB as they relate to reliability and validity. Option D is incorrect because a signed interpretation may not match written English.
Competency 005—(Instructional Planning and the Learning Environment): Apply knowledge of the diverse strengths and needs of learners who are deafblind to plan meaningful instructional opportunities that encourage social interaction and active engagement and promote a joy of learning in home, school, and community environments.
11. A ninth-grade student with 20/200 acuity in both eyes and a mild bilateral hearing loss receives inclusion support from a special education teacher in the general education classroom with collaborative consultation from a TDB. The student has a goal to demonstrate independence regarding accessibility needs. Which of the following strategies would most effectively support student access in the general education setting?
- providing a reinforcement schedule for the student when classroom expectations are met
- creating additional time during the school day to pre-teach and re-teach key academic concepts to the student as needed
- creating a self-monitoring checklist with the student to track the use of their current accommodations and supports
- encouraging the student to share any concerns about their accommodations with their general education teachers
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because the checklist requires the student to monitor their own use of accommodations and promotes independence regarding accessibility needs. This strategy would support the student in accessing and using their own accommodations and promote independence by requiring them to keep track of their use. Option A is incorrect because reinforcement for meeting expectations does not necessarily promote independent use of accommodations. Option B is incorrect because pre-teaching and re-teaching concepts may support student access, but it does not help the student meet the goal of demonstrating independence regarding accessibility needs. Option D is incorrect because while encouraging the student to share concerns about accommodations with their general education teachers may be a step toward independence regarding accessibility needs, this does not necessarily support student access in the classroom.
12. A TDB uses explicit and systematic approaches to develop students' incidental learning and communication. Which of the following activities would be most effective for a middle school student with cortical vision impairment (CVI), Phase II, and a moderate bilateral hearing loss?
- The TDB pairs the student with a peer to teach emergent concepts using look-touch-listen activities.
- The TDB provides repeated multisensory experiences with specialized materials and adaptations designed for the student.
- The TDB begins instruction using objects to promote familiarity and attention to the task.
- The TDB uses high-contrast pictures when teaching visual recognition of common objects found in the classroom.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because a multisensory approach allows a student with CVI to incorporate different sensory channels into the learning process. This will reduce visual fatigue and stress for the student and provide them with opportunities to use and develop sensory efficiency skills. Option A is incorrect because the teacher should provide direct and explicit instruction in skills and concepts. Option C is incorrect because relying only on real objects does not support the development of incidental learning. Option D is incorrect because relying only on two-dimensional materials for too long, even with high contrast, can be fatiguing for a student with CVI.
Domain III—Promoting Learning, Communication, and Independence
Competency 006—(The General Education and Expanded Core Curriculum): Apply knowledge of a variety of instructional strategies, methods, and meaningful activities to promote access, success, and independence in both the academic and expanded core curriculum for learners who are deafblind.
13. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A 16-year-old student who is deafblind has the following supports and accommodations in their Individualized Education Program (IEP):
- an educational interpreter to provide access to classroom instruction in American Sign Language (ASL) and interpret communication between the student and their teachers and peers
- an intervener to support the student with classroom tasks such as note taking and previewing new vocabulary, as well as by reviewing elements of the lessons that the student may have misunderstood from the initial lesson
- text enlargement software to help the student with accessing text on the computer or laptop for test taking and doing research on the Internet
- closed captioning
The student's transition plan includes a postsecondary plan to attend college. The TDB and student are working on self-advocacy goals as part of the expanded core curriculum (ECC). Which of the following strategies would best support the student in building self-advocacy skills in preparation for future employment and college?
- providing the student with a list of state and federal agencies that provide their specific accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
- connecting the student and their family with local support programs for children and adults with sensory disabilities
- explaining to the student the implications of their medical condition, including how to understand their vision and hearing test results
- working with the student to develop a brief video to explain how their current accommodations allow them access to and independence in their everyday activities
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because creating a video is student-driven and requires the student to self-advocate. The student must explain their accommodations and their benefits, preparing them to use these same skills of being able to self-advocate in the workplace and postsecondary education settings. Option B is incorrect because connecting the student and their family with support programs does not ensure that they will be used. Options A and C are incorrect because only providing this information to the student does not develop self-advocacy skills needed in the workplace or post-secondary settings.
14. A kindergarten student who is deafblind is learning to read braille. The student has a goal to develop fine-motor skills related to hand and finger strength. The TDB and occupational therapist (OT) coordinate various center-based activities to support the student's progress toward this goal. Which of the following activities would be most effective for developing the fine-motor skills related to this goal?
- organizing and placing letter shapes into boxes of different sizes
- popping the bubbles in bubble wrap to make a shape
- drawing lines on a piece of paper to simulate letter formation
- fitting wooden puzzle pieces together
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because pressing and popping bubble wrap strengthens finger muscles to build fine motor skills. This is an age-appropriate fine-motor activity related to hand and finger strength. Options A and D are incorrect because these activities focus on hand-eye coordination more than finger dexterity. Option C is incorrect because drawing lines on a piece of paper to simulate letter formation focuses on grip strength rather than hand to finger strength.
15. A high school student who is deafblind is fluent in American Sign Language (ASL) and has 20/60 vision with correction. The student has a goal to demonstrate understanding of their rights and responsibilities regarding community interpreter services. Which of the following activities would be most effective for the student to engage in to support their goal?
- becoming familiar with the training requirements for ASL interpreters
- learning how to engage with and schedule ASL interpreters
- attending Individualized Education Program (IEP) team meetings
- meeting with other students and adults who are Deaf
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because engaging with and scheduling their own ASL interpreters promotes student understanding and application of their rights and responsibilities regarding community interpreter services. This helps to prepare the student for eventual independent and appropriate use of interpreting services in the community as an adult. Option A is incorrect because understanding the training requirements for interpreters does not support the student in understanding their own rights and responsibilities regarding interpreting services. Option C is incorrect because attending IEP team meetings does not support the student in learning about interpreting services. Option D is incorrect because engaging with other peers and Deaf adults may not support the student in developing an understanding of their rights regarding interpreting services.
Competency 007—(Communication): Apply knowledge of a variety of linguistic and nonlinguistic communication modes and knowledge of the importance of identifying and developing learners' preferred mode of communication to promote learning, self-determination, and independence.
16. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A sign system, which is not a language of its own, was created to make spoken language visible. In this system, every word is signed and voiced, and morphological word endings (for example, -ed, -ing, -s) are used. Many of the signs are initialized, and concepts are not emphasized.
Which of the following sign systems best matches this description?
- Signing Exact English (SEE-II)
- American Sign Language (ASL)
- Conceptually Accurate Signed English (CASE)
- Protactile Language (PTL)
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because SEE-II is a sign system that represents the English language. It is not a language itself but a manual code for the English language that follows the rules of English grammar and uses initialized signs. Options B and D are incorrect because ASL and PTL are not sign systems but languages. Option C is incorrect because CASE is a blending of SEE-II and ASL and emphasizes concepts.
17. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A TDB is creating literacy materials for a ten-year-old, third-grade student who is deafblind and has multiple disabilities. The student has light perception in one eye, 20/400 acuity in the other eye after correction, and a moderate hearing loss in both ears. The student follows a routine-based schedule each day of the week as part of the student's self-contained classroom programming. Real objects are the student's designated and preferred literacy and learning medium. The student enjoys engaging in specific activities each day, including grooming, mathematics, cooking class, lunch, physical education, and music class.
The TDB wants to create functional literacy materials to help the student learn literacy-based one-to-one correspondence and symbolic representation, information recall, and time concepts. Which of the following materials would most appropriately support instruction in the literacy objectives for the student?
- an experience book with real objects related to daily activities for each school day corresponding to the student's daily routines
- a fictional story in auditory format presented on a tablet that describes a student who goes to school and has many adventures during the school day
- a digital slideshow with color pictures presented on a tablet that names and explains the purpose of each of the student's classes for each day of the week
- an experience book with print pictures of objects and braille text that describes unfamiliar or new learning activities on the student's schedule
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because an experience book using concrete materials that relate to the child's own life encourages the student to use and apply one-to-one correspondence and symbolic representation while also using the skills of information recall and time concepts as they record and talk about the events of the day. Options B, C, and D are incorrect because they do not incorporate real objects, which are the student's preferred literacy and learning medium.
Competency 008—(Technology: Low- and High-Tech): Apply knowledge of the role of both low- and high-tech devices and digital supports to promote independence, engagement, communication, and learning.
18. A second-grade student who is deafblind has a visual acuity of 20/100 and a mild-to-moderate sensorineural hearing loss. The student receives occupational therapy to address fine-motor skills and handwriting. Recent learning media assessment (LMA) results recommend introducing a speech-to-text device to the student to support written expression. Which of the following initial considerations would be most important to address when teaching the student to use a speech-to-text device?
- whether the student has a progressive or stable hearing loss
- the student's ability to speak at a consistent volume and enunciate clearly
- the student's current reading level and vocabulary
- whether the student can use a computer independently
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because speech-to-text technology requires clear and intelligible pronunciation. For an accurate transcription, the student's speech must be clear and intelligible and of an appropriate volume. Option A is incorrect because the stability of the student's hearing would not need to be addressed when teaching them to use the device. Options C and D are incorrect because reading and computer skills are not as important as the student's speaking skills when teaching them to use a speech-to-text device.
19. In paired instructional lessons, a student who is deafblind demonstrates success with a digital picture communication device after a partial physical prompt. Which of the following prompts in the most-to-least prompting hierarchy should the TDB use next to support the student's independence with the device?
- full physical
- visual
- direct verbal
- modeling
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because according to the most-to-least prompting hierarchy, modeling would be the next least restrictive support to promote independence following a partial physical prompt. Because the student has been successful with a partial physical prompt, a less intrusive prompt should be used next to support the student's independence with the device. Option A is incorrect because a full physical prompt would be more restrictive than a partial physical prompt. Option B is incorrect because a visual prompt would be the least restrictive support before independence with the device. Option C is incorrect because a direct verbal prompt should not be attempted until the student demonstrates success with modeling and gestural prompts.
20. A TDB and a teacher of students with visual impairments (TVI) work with an eight-year-old student who has Stargardt disease to transition from a tactile symbol calendar system paired with braille to using mainly braille cards in the calendar system. The student has learned to read all the labels in uncontracted braille and is progressing with braille instruction. Which of the following strategies for incorporating assistive technology devices would promote the student's braille learning at this time?
- providing a SMART Brailler® for the student to develop written expression using the vocabulary learned in braille
- introducing a braille QWERTY keyboard for the student to develop their keyboarding skills and writing
- beginning instruction using a slate and stylus for the student to develop writing skills
- incorporating a braille calculator for the student to practice math computation and number recognition
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because a SMART Brailler provides multisensory feedback by displaying brailling and providing auditory output of what the student types. An assistive technology device that provides immediate feedback would be most appropriate to promote the student's braille learning. Options B, C, and D are incorrect because they do not provide immediate feedback to promote the student's braille learning.
Domain IV—The Educator as a Professional
Competency 009—(Collaboration and Consultation): Apply knowledge of techniques for fostering active inquiry, collaboration, instructional coaching, and supportive interaction between professionals, family members, interveners, paraeducators, and learners who are deafblind.
21. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
The Individualized Education Program (IEP) team completes a reevaluation for a third-grade student whose current placement is a self-contained functional skills classroom. The following new information is included in the report:
- visual impairment due to high myopia resulting in a best corrected acuity after surgery of 20/80 OU
- initial audiology report provided by the family indicating that the student has a moderate hearing loss in the right ear due to a perforated eardrum and a current mastoiditis infection that was not detected in a timely manner
- hearing aids to be considered in the future pending resolution of the mastoiditis
- speech-language pathologist (SLP) indicates a need for continued speech therapy due to significant receptive and expressive speech delays
Which of the following actions should the TDB take to support the IEP team in considering the student's current evaluation data as part of their decision-making process?
- providing information regarding the alignment of the student's current IEP goals to the grade-level curriculum to support instructional programming
- providing information about the impact of the student's dual sensory loss on access to communication and instruction to inform instructional programming
- providing a comprehensive plan for the student's instructional program and accommodations for each service provider to follow
- providing examples of the types of augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices based on the student's evaluation results and the instructional program
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the role of the TDB on the IEP team is to clarify questions regarding eligibility for services and programming and to collaborate to determine the student's need for specially designed instruction. The TDB has a unique expertise in evaluation, communication, and instructional strategies used with students who have dual sensory impairment. Options A, C, and D are incorrect because the student's IEP goals, accommodations, and use of assistive technology would require input from various other service providers.
22. The family of a seven-year-old student who is deafblind meets with the Individualized Education Program (IEP) team. The parents/guardians inquire about various interventions and programs that may be appropriate for them as they work to support their child's communication and learning goals. They ask the team, "What interventions does the research recommend to effectively support our child's social skills and language development?" Which of the following responses by the TDB would be most appropriate to answer their question?
- "Providing the student with many opportunities to explore, compare, and contrast a variety of objects to understand their function."
- "Building relationships with peers, role models, and eventually mentors with similar sensory access needs has positive psychosocial benefits for students from childhood through adulthood."
- "Learning to set attainable goals, working hard to reach them, and having support from their family and friends helps students identify their future goals."
- "Experiencing a learning environment that is consistent and provides discipline and structure helps students with disabilities learn to meet any challenges."
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because research shows the positive impact of relationships with peers and adults on the quality of life of individuals who are deafblind. Connections with others with similar sensory access needs, through peer relationships, role models, and/or mentoring helps to build resilience and has a positive impact on self-concept. Option A is incorrect because this may help language development but not social skills. Options C and D are incorrect because setting goals and having a consistent learning environment may be important, but they are not as impactful as building relationships on the development of social skills and language.
Competency 010—(Educator Responsibilities, Ethical Practice, and Professional Growth): Understand teaching as a profession, maintain and adhere to ethical standards and professional conduct, and understand the value of reflective practice and professional growth.
23. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
According to the IEP Quality Indicators for Students who are Deafblind (Texas Deafblind Outreach 2003; revised 2023), ten content areas should be addressed in a well-designed Individualized Education Program (IEP) for a student who is deafblind to specifically address their individualized needs. An incomplete list of these quality indicators is shown below.
- Etiology
- blank
- blank
- Communication
- Calendar System
- Behavior
- Orientation and Mobility (O&M)
- Related and Supplemental Services
- Transition Planning
- A Teaming Process Plan
Which two indicator categories complete the list of content areas to address to ensure that an IEP is well designed and appropriate to the individualized needs of a student who is deafblind?
- Technology Sign Language Instruction
- Functional Literacy Braille Instruction
- Access to Information Social Issues
- Expanded Core Curriculum Self-Advocacy
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because according to the IEP Quality Indicators for Students who are Deafblind, Access to Information and Social Issues should be addressed in the IEP and represent distinct areas of need. The IEP teams for students who are deafblind must consider specific effects on various areas, including access to information and social relationships, to create appropriate programs for these students. Option A is incorrect because technology and sign language instruction are part of Access to Information and Communication. Option B is incorrect because functional literacy and braille instruction are addressed in Communication. Option D is incorrect because elements of the Expanded Core Curriculum (ECC) include several of the content areas (e.g., O&M, communication). It would therefore be redundant to include the ECC and self-advocacy as categories.
24. An eleventh-grade student who is deafblind has no light perception (NLP) and moderate-to-severe hearing loss. The student consistently wears hearing aids and is independent in the care of the hearing aids. The student has functional goals in the areas of self-care, socialization, daily living, and prevocational skills. The student uses a weekly calendar system with object symbols, as well as pointing, some functional signs, and gestures. The student matches, categorizes, and completes work jobs in the classroom as part of prevocational training transition goals, and maintains attention with support. The student's postsecondary transition plan identifies continued development of work skills and daily living skills. For this student, the recommendation of the least restrictive environment (LRE) would most likely be which of the following settings?
- general education classrooms
- blended resource special education and general education classrooms
- a life skills classroom
- a substantially separate program located within the school district
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because in a life skills classroom setting, the instructor can most effectively provide specially designed instruction (and materials) aligned with the student's prevocational transition plan for continued development of work-related and daily living skills. Options A and B are incorrect because the student has prevocational training goals and daily living skills goals that would likely not be able to be effectively addressed in the general education or a blended resource setting. Option D is incorrect because separate programming would be more restrictive than a life skills classroom, which would meet the student's needs.
25. Parents/guardians have provided written consent for a Full and Individual Initial Evaluation (FIIE) for their child. According to the Special Education Initial Referral Timeline, the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee must meet to review the comprehensive evaluation results and determine eligibility:
- within 30 days after the parents/guardians were provided the Prior Written Notice for evaluation.
- not later than the 45th school day following the date the district received the written parental consent.
- within 30 calendar days from the date the comprehensive evaluation report is completed.
- not earlier than 45 days after the parents/guardians were provided the Parent's Guide to the Admission, Review, and Dismissal Process document.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because an ARD meeting must be held within 30 calendar days after the FIIE report is completed. There is a specific timeline for the various components of the FIIE process based upon when the school district receives written consent for an FIIE. Options A, B, and D are incorrect because the evaluation must be completed within 45 days of the parental consent for evaluation, followed by the ARD meeting to review the results and determine eligibility within 30 days of the completed evaluation.
Additional Selected-Response Questions
This section includes additional sample selected-response questions for you to review in preparation for the exam. The correct answer is provided for each question below.
Domain I—Knowledge of Learners and the Visual, Auditory, Tactile, and Sensory Systems
Competency 001—(Foundations): Apply knowledge of key philosophical, historical, and legal foundations in the education of learners who are deafblind.
26. Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic condition that affects the layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. RP is a primary condition associated with:
- Usher syndrome.
- Prader-Willi syndrome.
- CHARGE syndrome.
- Stickler syndrome.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
27. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
The family of a student diagnosed with Usher syndrome Type 2 moves to Texas from another state prior to the new school year. The student's current Individualized Education Program (IEP) identifies a primary eligibility of deaf/hard of hearing (DHH) and a secondary eligibility of multiple disabilities (MD). The parents/guardians present their child's IEP and necessary eligibility and assessment documentation to the Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee. During the meeting, the following discussion occurs.
School Representative: We are very excited to have you and your child join our school community! Thank you for the copy of the IEP to help provide a smooth transition to this process.
Parent/Guardian: Thank you! We just want our child, P.J., to get acclimated to new teachers and staff, make new friends, and keep making progress to achieve his vision, hearing, and academic goals.
School Representative: I see that P.J. has a primary eligibility of DHH, and secondary eligibility of MD. P.J.'s schedule of services includes DHH and VI services, speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, assistive technology, audiology, and orientation and mobility. As a team, we will review the existing evaluation data and would like to consider eligibility for special education services under the category of deafblind.
Which of the following statements would be most accurate for the school representative to use in describing the rationale for a change of eligibility category for P.J. at this time?
- There is the possibility no change would be proposed in P.J.'s current placement or service time as listed on the IEP.
- There is no benefit from having two eligibility categories identified on the IEP as far as P.J.'s goals and placement are concerned.
- There are unique considerations and resources to support both P.J. and the family that would be more accessible to meet their needs now and in the future.
- There are service delivery options that are unavailable to P.J. due to the multiple eligibility categories currently listed.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Competency 002—(Learners' Strengths and Needs): Apply knowledge of the complex and unique effects of combined vision and hearing impairment as well as the strengths of the tactile sense of learners who are deafblind.
28. A kindergarten student with CHARGE syndrome frequently bumps into things, sometimes purposefully, and has difficulty sitting in a chair without sliding down or falling out of it. These characteristics are most likely related to which of the following aspects of CHARGE syndrome?
- executive function and motivation delays
- muscle spasticity and nerve pain
- poor proprioception and low muscle tone
- hypersensitivity and joint swelling
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
29. A three-year-old child who has a pet dog is able to look at pictures of different animals, identify a dog, and share that a dog barks. Which of following skills is the child using to identify and describe a dog in this scenario?
- visual closure
- abstract thinking
- visual memory
- problem solving
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Competency 003—(Anatomy/Physiology of the Auditory, Visual, Tactile, and Sensory Systems): Understand the key components and functions of the human auditory, visual, tactile, and sensory systems.
30. A TDB provides systematic vocabulary instruction to a student with a central visual field loss and a profound hearing loss. The teacher presents two objects and two cards in braille with a sentence describing the objects to the student. The student picks up one object at a time, holds it up to the light, turns it around, and shifts it from hand to hand, squeezing it. Then the student smells the object and rubs it against their cheeks and forehead. The student then places the object on the corresponding card to identify it. The student's actions in this activity demonstrate which of the following concepts regarding the role of the intact and residual sensory systems on learning for students with combined sensory loss?
- Instructional strategies that encourage tactile and sensory exploration have been shown to promote the concept and language development of students who are deafblind.
- The use of hands-on manipulatives supports instruction through scaffolding for students who are deafblind.
- Sensory exploration of the environment is most effective when combined with assistive technology to promote engagement and access for students who are deafblind.
- Integrating familiar manipulatives provides increased understanding for guided and independent practice during instruction for students who are deafblind.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
31. Which of the following key structures of the auditory system also plays a major role in the vestibular system?
- pinna
- hair cells
- stapes
- tympanic membrane
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
32. Which of the following functions does the visual cortex serve in the process of visual perception?
- protecting the inside eye structures from harmful materials
- controlling the amount of light that enters the eyes
- transferring visual information to the occipital lobe
- processing visual stimuli received from the optic tracts
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Domain II—Assessment, Instructional Planning, and the Learning Environment
Competency 004—(Evaluation and Assessment): Apply knowledge of the educational evaluation and assessment process to determine a learner's strengths and needs, and apply appropriate assessment strategies in the learner's preferred mode of communication to support the learner.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.A six-year-old student's responses to sensory stimuli are evaluated using a sensory-based assessment. Below are the results of the assessment:
1. Vestibular: Student enjoyed rocking back and forth as evidenced by smiling but showed an aversion to side-to-side rocking by crying out.
• Further probes needed: None at this time.
2. Proprioception: Student really enjoyed deep pressure on the arms and legs, which was indicated by quieting and calming.
• Further probes needed: None at this time.
3. Tactile: Student loved a variety of squishy balls; some had a gelatinous substance inside, others had smaller balls inside the bigger ball. The student disliked wet textures.
• Further probes needed: None at this time.
4. Visual: Student noticed bright lights or spotlighting mylar materials; when materials were presented without a light component student did not notice visually presented materials.
• Further probes needed: None at this time.
5. Olfactory: Student did not have a reaction to any of the scents presented. Student did not put any objects presented up to their nose.
• Further probes needed: Possible lack of olfactory sense needs further discussion.
6. Gustatory: Not applicable; student is G-tube fed.
• Further probes needed: After swallow study is conducted, may present a taste on the student's tongue.
7. Auditory: Student showed more interest in objects presented that had an auditory component.
• Further probes needed: All objects presented also had a light component; try again without lights to see if student is drawn to lights, sound, or both.
8. Causality: Student is still learning causality.
• Further probes needed: None at this time.
33. Based on this sensory assessment, which of the following activities would be an appropriate motivator for this student?
- engaging in a light pressure routine
- playing with a sensory bin filled with water beads
- swinging with a weighted blanket
- rolling a hard ball with a bumpy surface
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
34. A TDB plans to evaluate a 12-year-old student with congenital rubella syndrome for an upcoming functional vision evaluation/learning media assessment (FVE/LMA) and communication evaluation. The student has multiple disabilities, including a profound hearing loss. The student wears bilateral hearing aids and will respond by vocalizing and with prelinguistic communication to familiar voices and tactile cues. The student's latest eye report indicates no light perception (NLP) in both eyes. Which of the following evaluation tools would be most appropriate for assessing this student's strengths and current areas of functioning?
- Assessment of Deafblind Access to Manual Language Systems
- Child-Guided Strategies: The van Dijk Approach to Assessment
- Barraga Visual Efficiency Program
- Callier-Azusa Scale
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
35. A TDB works with an educational diagnostician to assess a seven-year-old student who has a profound hearing loss with best corrected visual acuity of 20/400 and a restricted visual field. According to Dr. Jan van Dijk's Child-Guided Assessment protocol, it is important to address which of the following domains first in the observational, child-guided method?
- problem solving
- approach withdrawal
- biobehavioral state
- social interaction
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Competency 005—(Instructional Planning and the Learning Environment): Apply knowledge of the diverse strengths and needs of learners who are deafblind to plan meaningful instructional opportunities that encourage social interaction and active engagement and promote a joy of learning in home, school, and community environments.
36. Read the excerpt below from the Individualized Education Program (IEP) of a fourth-grade student who is deafblind; then answer the question that follows.
Present Level of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP): The student often sits alone during the daily recreation/leisure choice time center activities. The student refuses or ignores any verbal or object prompts presented by the teacher or intervener to engage in a preselected activity. The special education teacher is collaborating with the TDB to identify a strategy to encourage the student's engagement in recreation/leisure choice time.
Goal: By the end of the IEP year, when provided with one verbal or tactual prompt and a choice board with two objects, the student will choose one preferred recreation/leisure activity in 4/5 trials.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate method to support the student's engagement in a recreation/leisure activity?
- offering the student the opportunity to make a choice between a preferred and a non-preferred activity
- allowing the student to sit alone during the recreation/leisure choice time and waiting for the student to engage without any staff intervention
- bringing the materials and the activity to where the student is sitting and having other students engage in the activity in the student's personal space
- sending the student with the intervener to work on other IEP goals during this time until the student is ready to engage in recreation/leisure activities with peers
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct.
37. A TDB collaborates with general education teachers and speech-language pathologists to create structured communicative interactions across school settings. Which of the following rationales best supports the use of this strategy and practice for students with dual sensory loss?
- Structured communicative interactions promote students' independent engagement in social activities.
- Structured communicative interactions encourage students to develop social routines.
- Structured communicative interactions allow students to acquire content-area knowledge in context to support generalization of skills.
- Structured communicative interactions provide incidental learning opportunities for students to acquire knowledge and social skills.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct.
38. A TDB uses a calendar system with a fifth-grade student to support daily transitions. The anticipation calendar consists of two very distinct containers on the student's desk with items representing the next activity in the student's day. The teacher notes that after lunch, the student uses the anticipation calendar to move the spoon from one container to the other. The student's action provides evidence that they have developed which of the following concepts?
- tactile memory
- object permanence
- past and future
- action-reaction
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Domain III—Promoting Learning, Communication, and Independence
Competency 006—(The General Education and Expanded Core Curriculum): Apply knowledge of a variety of instructional strategies, methods, and meaningful activities to promote access, success, and independence in both the academic and expanded core curriculum for learners who are deafblind.
39. A student with high myopia and congenital severe-to-profound bilateral hearing loss uses cochlear implants and wears glasses. Which of the following activities most effectively promotes the student's ability to access visual cues to support their auditory comprehension when learning new vocabulary?
- prompting the student to check the functioning of their assistive listening device
- ensuring the student has access to the speaker's face as information is spoken
- sitting beside the student while giving the student verbal directions
- using objects to depict the meaning of content-specific terms
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
40. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
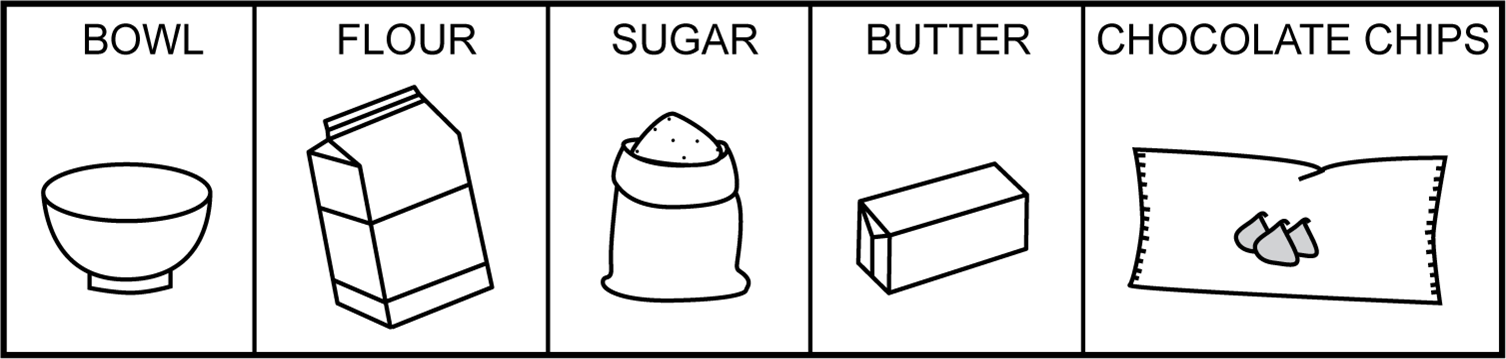
A middle school student with optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH) and a moderate bilateral hearing loss uses amplification and is learning a multistep, sequenced routine. The TDB introduces the student to baking cookies by using a sequence box. The TDB initiates the conversation by verbally labeling and tactually exploring each item with the student in the sequence box below.
Image of a sequence box containing items and ingredients to be used for the recipe including: a bowl, a bag of flour, a bag of sugar, a stick of butter, and a bag of chocolate chips.
During the routine, the student becomes excited when recognizing the sugar and begins tasting it. The TDB extends the discussion with the student by touching and repeating the word SUGAR and teaching its corresponding sign. The primary purpose of teaching this routine is to:
- encourage the student to interact socially with others through a preferred-learning task.
- integrate larger topics of language, concept development, and conversation in a meaningful activity.
- enable the student to complete tasks by incorporating strategies into a structured routine.
- include a variety of communication systems to encourage active participation in a conversation.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
Competency 007—(Communication): Apply knowledge of a variety of linguistic and nonlinguistic communication modes and knowledge of the importance of identifying and developing learners' preferred mode of communication to promote learning, self-determination, and independence.
41. Which of the following principles is known as the First Principle of Protactile Language (PTL)?
- Protactile communication is a means of sharing experiences.
- When sharing information, be sure to include the sources of the information.
- Any time space is used, it should be contact space, not air space.
- In Protactile the best way to communicate is through touch.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
42. A four-year-old child with 20/400 acuities OU has a profound bilateral hearing loss and communicates at the prelinguistic stage. The Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee is developing goals to promote the child's communication and emergent literacy skills. After reviewing recent assessment data, and on recommendation of the TDB and speech-language pathologist (SLP), the team plans to introduce real objects and tactile symbols to develop the child's receptive and expressive communication. Which of the actions should the teachers take first to develop the child's understanding of real objects and tactile symbols as communication?
- developing cognitive skills related to theory of mind
- building understanding of concrete representations
- promoting functional vision to support visual processing
- encouraging emergent sensory efficiency and motor skills
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct.
43. A sixth-grade student who has low vision with a congenital bilateral mild hearing loss has targeted goals to develop functional hearing and listening skills. The TDB regularly uses a modified auditory sandwich technique to teach new routines and give directions. When using this technique, the purpose of restating a verbal direction or statement after presenting a tactile cue is to:
- observe the student's initial level of auditory attention.
- emphasize the importance of the student's participation in the activity.
- reinforce and strengthen the student's auditory input and processing.
- prevent misinterpretation of the direction cues by the student.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct.
Competency 008—(Technology: Low- and High-Tech): Apply knowledge of the role of both low- and high-tech devices and digital supports to promote independence, engagement, communication, and learning.
44. A middle school student uses various technology accommodations, including their cell phone, school laptop, handheld magnifier, digital modulation system (DM system), and personal hearing aids. The student's intervener is primarily responsible for managing the everyday equipment. The student is independent in the care and maintenance of their hearing aids and cell phone. The Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) committee has developed goals for the student to develop responsibility for their technology, including transporting equipment from class to class and ensuring the devices are charged. Which of the following strategies would be most effective for initial instruction on maintaining personal technology?
- creating a daily written checklist for maintenance steps for the equipment for the student to complete and turn in to a designated staff person at the end of the day
- developing a plan with the student to manage one piece of equipment at a time with the least intrusive monitoring system that can be faded as the student develops independence
- asking the student's parents/guardians to encourage the student's independence in their everyday use of their devices and technology at home and at school
- discussing with the student the importance of appropriate maintenance and use of their devices while developing a plan for the use and care of their devices
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
45. A disadvantage of using a tablet as a student's primary assistive technology device to access the learning management system is that:
- options for voicing and speech are limited.
- access to a strong Internet connection is needed.
- color preferences may not be adequate or adjustable.
- optical character recognition is inconsistent.
- Answer
- Option B is correct.
Domain IV—The Educator as a Professional
Competency 009—(Collaboration and Consultation): Apply knowledge of techniques for fostering active inquiry, collaboration, instructional coaching, and supportive interaction between professionals, family members, interveners, paraeducators, and learners who are deafblind.
46. A middle school student with CHARGE syndrome is experiencing difficulty with balance while sitting at their desk for long periods of time. The educational interpreter is positioned 3 feet away and uses large expressive signs that are hard for the student to visually track. The student is experiencing a great deal of fatigue due to their sensory needs and the extra energy used to access the visual and auditory information. Which of the following actions by the TDB would most quickly and effectively address the student's access to classroom instruction while also reducing the fatigue that the student is experiencing?
- building in peer-supported learning opportunities during the school day
- administering a functional evaluation to determine optimal signing space for the interpretation
- allowing the student to take more frequent breaks from classroom instruction
- trialing hand-tracking strategies that allow the student to have tactile access to the interpretation
- Answer
- Option D is correct.
47. A student who is deafblind will age out of school-based services at the end of the current school year and is getting ready to enroll at the local community college for the summer. The student shares with the TDB that the family is having difficulty finding an affordable way to obtain a tablet device with adequate capacity to allow the student access to print materials. Which of the following resources should the TDB suggest the family contact first for support with obtaining assistive technology for the student's postsecondary endeavors?
- Texas Workforce Commission (TWC) Vocational Rehabilitation Services
- Texas Health and Human Services (HHS) Blind Children's Vocational Discovery and Development Program (BCVDDP)
- Deaf Blind with Multiple Disabilities (DBMD) Waiver Program
- The National Federation of the Blind (NFB)
- Answer
- Option A is correct.
48. A third-grade student with cerebral palsy (CP), cortical visual impairment (CVI), nystagmus, and seizures uses a wheelchair. The student has auditory neuropathy, with communication at the prelinguistic stage. The TDB and the student's intervener discuss strategies to develop competent communication partners and ways to create meaningful interactions for the student. Which of the following activities should be conducted first to facilitate positive interaction, communication, and bonding between the intervener and the student?
- The intervener should read the student's records and all information regarding the student's visual diagnosis and hearing condition.
- The TDB should assist the intervener in getting to know the student's likes and dislikes, how the student engages with the environment, and the student's strengths.
- The intervener should talk with the student's family and related service providers to understand their expectations for the student.
- The TDB should provide the intervener with the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals and share their expectations for the student's learning.
- Answer
- Option B is correct.
Competency 010—(Educator Responsibilities, Ethical Practice, and Professional Growth): Understand teaching as a profession, maintain and adhere to ethical standards and professional conduct, and understand the value of reflective practice and professional growth.
49. An eleventh-grade student and their parents/guardians attend the annual Individualized Education Program (IEP) team meeting. The student is blind, with a moderate hearing loss due to Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA). The student wears hearing aids and is a fluent braille reader. The student's preferred mode of communication is listening and spoken language (LSL), and the student uses a refreshable braille display for written communication. The student has a postsecondary goal to attend a vocational program at the local community college. To directly support the student's postsecondary goal, the TDB should ensure that the student and the parents/guardians have knowledge of and access to which of the following resources?
- Texas Workforce Commission (TWC) Vocational Rehabilitation Services
- The Arc of Texas
- Texas Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)
- Coalition of Texans with Disabilities (CTD)
- Answer
- Option A is correct.
50. When developing an Individualized Education Program (IEP) for students who are deafblind, which of the following topics must be considered and is required to be discussed by the IEP team?
- how to create activities and materials for visual and auditory efficiency based on the needs of the student
- the work products that will identify the student's progress on classwork, projects, and assessments
- how to provide training and professional development for staff on the impact that a dual sensory loss has on a student's educational progress
- the full range of placements and types of supports needed for the student to access the curriculum and setting
- Answer
- Option D is correct.